Design and synthesis of chiral DOTA-based MRI contrast agents with remarkable relaxivities
- PMID: 37973896
- PMCID: PMC10654417
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-023-01050-w
Design and synthesis of chiral DOTA-based MRI contrast agents with remarkable relaxivities
Abstract
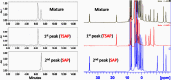
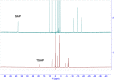
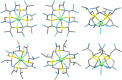
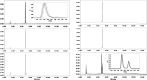
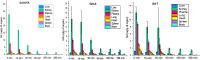
Due to the adverse effects of de-metallation in past concerning FDA-approved gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs), researchers have been focusing on developing safer and more efficient alternatives that could avoid toxicity caused by free gadolinium ions. Herein, two chiral GBCAs, Gd-LS with sulfonate groups and Gd-T with hydroxyl groups, are reported as potential candidates for magnetic reasonance imaging (MRI). The r1 relaxivities of TSAP, SAP isomers of Gd-LS and SAP isomer of Gd-T at 1.4 T, 37 °C in water are 7.4 mM-1s-1, 14.5 mM-1s-1 and 5.2 mM-1s-1, respectively. Results show that the hydrophilic functional groups introduced to the chiral macrocyclic scaffold of Gd-T and Gd-LS both give constructive influences on the second-sphere relaxivity and enhance the overall r1 value. Both cases indicate that the design of GBCAs should also focus on the optimal window in Solomon-Bloembergen-Morgan (SBM) theory and the effects caused by the second-sphere and outer-sphere relaxivity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gadolinium(III) complexes of mono- and diethyl esters of monophosphonic acid analogue of DOTA as potential MRI contrast agents: solution structures and relaxometric studies.Dalton Trans. 2007 Jan 28;(4):493-501. doi: 10.1039/b612876a. Epub 2006 Dec 20. Dalton Trans. 2007. PMID: 17213936
-
T1 relaxivities of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance contrast agents in human whole blood at 1.5, 3, and 7 T.Invest Radiol. 2015 May;50(5):330-8. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000132. Invest Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25658049
-
Enhancing T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast with internalized gadolinium(III) in a multilayer nanoparticle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 3;114(27):6960-6965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701944114. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28630340 Free PMC article.
-
MRI contrast agents: basic chemistry and safety.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012 Nov;36(5):1060-71. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23725. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. PMID: 23090917 Review.
-
Cyclen-based Gd3+ complexes as MRI contrast agents: Relaxivity enhancement and ligand design.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 15;24(22):5663-5684. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.09.069. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27729196 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Based T1 Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;15(1):33. doi: 10.3390/nano15010033. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39791792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology in inflammation: cutting-edge advances in diagnostics, therapeutics and theranostics.Theranostics. 2024 Apr 8;14(6):2490-2525. doi: 10.7150/thno.91394. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38646646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gd-GQDs as nanotheranostic platform for the treatment of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer.Med Oncol. 2024 Jul 22;41(8):205. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02431-4. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39037549
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

