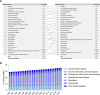
The impact of fibrotic diseases on global mortality from 1990 to 2019
- PMID: 37974206
- PMCID: PMC10652519
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04690-7
The impact of fibrotic diseases on global mortality from 1990 to 2019
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources