Tips and Tricks to Safely Perform an Endoscopic Endonasal Trans-Sphenoidal Pituitary Surgery: A Surgeon's Checklist
- PMID: 37974746
- PMCID: PMC10645713
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-03834-x
Tips and Tricks to Safely Perform an Endoscopic Endonasal Trans-Sphenoidal Pituitary Surgery: A Surgeon's Checklist
Abstract
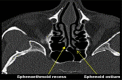
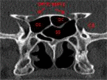
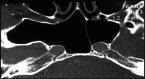
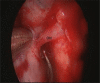
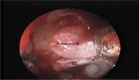
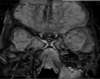
The authors aimed to develop an extensive preoperative checklist of CT scan findings during endoscopic access to the ventral skull base and implement it in clinical practice. A comprehensive literature review was conducted to identify the radiological landmarks crucial to endoscopic skull base surgery. Four electronic databases were searched: PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Google Scholar using search terms/keywords such as "radiological landmarks," "endoscopic skull base surgery," "CT scan," "pituitary surgery," "anatomical variations," "internal carotid," "optic nerve," "sphenoid sinus," "pneumatization," "dehiscence," and "protrusion". Inclusion criteria were limited to original articles and systematic reviews published in English, between the years 2000 and 2021, which pertained to the radiological landmarks to be identified during endoscopic skull base surgery. Full-text articles were retrieved and collated into a narrative review focused on a 12-item checklist the authors agreed upon. The mnemonic "O ROAD TO SELLA" was used to represent the checklist and include the following landmarks: Sphenoid Ostium, Sphenoid Rostrum, Onodi cells, Anatomic variations of the sphenoid sinus, Distance between the carotids, Tumor characteristics, Optic nerve dehiscence/protrusion, Septation/insertion of the sphenoid sinus, Entrance to the sellar floor, Lateral recess of the sphenoid sinus, cLinoid process pneumatization, and internal carotid Artery dehiscence/protrusion. The checklist is designed to be used by attending physicians, fellows, and residents and the authors intend to implement it into electronic medical records at the institution's medical center to monitor the outcomes of EEPS after implementation.
Keywords: Anatomical variations; Endoscopic sinus surgery; Pituitary surgery; Preoperative checklist; Radiological landmarks.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiological features for the approach in trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgery.Pituitary. 2017 Aug;20(4):395-402. doi: 10.1007/s11102-017-0787-9. Pituitary. 2017. PMID: 28154960
-
Anatomic Variations of the Sphenoid Sinus and Their Impact on Trans-sphenoid Pituitary Surgery.Skull Base. 2008 Jan;18(1):9-15. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-992764. Skull Base. 2008. PMID: 18592020 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution computed tomography analysis of variations of the sphenoid sinus.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2013 Apr;74(2):82-90. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1333619. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2013. PMID: 24436893 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Onodi cell and new classification of sphenoid sinus for endoscopic sinus surgery.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Nov;5(11):1068-76. doi: 10.1002/alr.21567. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 26097234 Review.
-
Is Complex Sphenoidal Sinus Anatomy a Contraindication to a Transsphenoidal Approach for Resection of Sellar Lesions? Case Series and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2017 Apr;100:173-179. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.12.123. Epub 2017 Jan 5. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28065874 Review.
References
-
- Kassam AB, Prevedello DM, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Thomas A, Gardner P, Zanation A, Duz B, Stefko ST, Byers K, Horowitz MB. Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery: analysis of complications in the authors' initial 800 patients. J Neurosurg. 2011;114(6):1544–1568. doi: 10.3171/2010.10.JNS09406. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
