Incidence of Airway Complications in ICU
- PMID: 37974766
- PMCID: PMC10645749
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-03850-x
Incidence of Airway Complications in ICU
Abstract
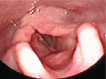
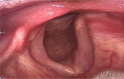
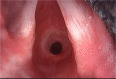
To show the incidence of airway complications in ICU. Endotracheal intubation is an essential skill performed by multiple medical specialists to secure a patient's airway as well as provide oxygenation and ventilation through the oral route or nose. The goal of endotracheal intubation in the emergency setting is to secure the patient's airway and obtain first-pass success. There are many indications for endotracheal intubation, including poor respiratory drive, questionable airway patency, hypoxia, and Hypercapnia. These indications are assessed by evaluating the patient's mental status, conditions that may compromise the airway, level of consciousness, respiratory rate, respiratory acidosis, and level of oxygenation. In the setting of trauma, a Glasgow Coma Scale of 8 or less is generally an indication for intubation. There are many different complications of intubation as hoarseness of voice, dental injuries, arytenoid dislocation, laryngeal stenosis, tracheal stenosis and tracheomalacia. . 150 patients who were sat in the ICU that developed certain complications. 86 patients (57.3%) were sitting in the ICU develoed certain complications. Liver diseases were the main cause of ICU admission 34 (22.7%) patients then shock 32 (21.3%) patients. Blockage of endotracheal tube was the main ICU complications 18 (12%) patients then sinusitis 16 (10.7%) patients. Endotracheal intubation is a lifesaving procedure and its complications are significant problems in ICUs. A successful procedure of intubation avoids complications. Skilled endotracheal intubation in the ICU decreases the complications.
Keywords: Endotracheal intubation; Post-intubation tracheal stenosis; Tracheoesophageal fistula; Tracheomalacia.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Casey DF. Tracheal intubation. In: Fowler GC, editor. Pfenninger and fowler's procedures for primary care. 4. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020.
-
- Driver BE, Reardon RF. Tracheal intubation. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, editors. Roberts and Hedges' clinical procedures in emergency medicine and acute care. 7. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2019.
-
- Hartman ME, Cheifetz IM (2020) Pediatric emergencies and resuscitation. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier
-
- Amr N, Samy A, ABD EL-AZIZ A, Voice disorders after intubation: the importance of intra-operative monitoring and controlling of endo-tracheal tube cuff pressure in reducing intubation-related complications. Med J Cairo Univ. 2018;86(5):2849–2860.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials