A Comparative Study Between Anterior-Posterior and Superior-Inferior Flap Suturing Technique in Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy at our Tertiary Institution
- PMID: 37974788
- PMCID: PMC10646028
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-03860-9
A Comparative Study Between Anterior-Posterior and Superior-Inferior Flap Suturing Technique in Endoscopic Dacryocystorhinostomy at our Tertiary Institution
Abstract
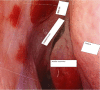
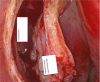
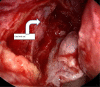
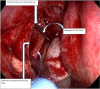
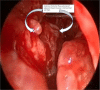
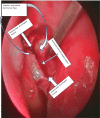
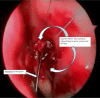
The Nasolacrimal sac inflammation, also known as dacryocystitis, is frequently accompanied by nasolacrimal duct blockage at the confluence of lacrimal sac and duct. Treatment of choice for dacryocystitis is dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), which can be done through external approach and endoscopic approach. The endoscopic DCR has distinct advantage over the external DCR as there is no facial scar& also it maintains the pump action. We have used flap suturing technique of endoscopic DCR in our study where in lacrimal sac medial flap is sutured to nasal mucosal lateral flap wherein patients were selected into either of the two groups such as Anterior-Posterior type (group A) and Superior-Inferior type (group B) of Flap suturing technique. Aim and objectives of the study were to compare the subjective and objective success rate between group A & B of flap suturing used in endoscopic DCR & to compare the success rate of our techniques with other techniques in literature. Our study was Duration based prospective observational study with a Duration of one year from June 2021 till June 2022 with study population comprised of patients in age group of 20 to 70 years, with complaints of watering of eye (epiphora) attended ENT Department of our institute during this one year. Study population comprised of Total of 86 patients (100 eyes) of which 45 patients (51 EYES) underwent anterior- posterior flap suturing (Group A) and 41 patients (49 eyes) underwent superior- inferior flap suturing (Group B) technique of endoscopic DCR The mean age ± standard error of mean was 45.1765 ± 1.5 and 49.0816 ± 1.9 in group A & B respectively,which was not statistically significant (p value = 0.994). The male and female patients in group A & B was 27.45%,72.54% and 34.69%,65.30% respectively which was not statistically significant (p value = 0.434). At each follow‑up, subjective success rate was more in group A that indicated a better trend of success for that group. However, the difference in the success rate was not statistically significant.The objective success rate between the two groups were more or less similar & was not statistically significant. The subjective success rate in both Anterior-Posterior type (group A)and Superior-Inferior type (group B) of Flap suturing techniques of endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy were more or less similar with regards to absence of epiphora but objective success rate with regards to the patency, were almost similar with a shift of trend from Group A to group B at 6 months follow up and we also found that complications in both the groups were very few, without statistically significant difference between them. In terms of success rate and complication,The endoscopic DCR with flap suturing technique found to be more or less similar with previous techniques of DCR described in the literature.
Keywords: Dacryocystorhinostomy; Endoscopic; Lacrimal flap; Nasal flap; Suturing.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll the authors declare that they have not any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dacryocystorhinostomy.2023 Aug 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Aug 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32496731 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparing the success rate of external dacryocystorhinostomy with anterior flap versus flap excision in managing chronic dacryocystitis.Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2023 May 31;12(1):1-8. doi: 10.51329/mehdiophthal1464. eCollection 2023 Spring. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37641669 Free PMC article.
-
External dacryocystorhinostomy: Double-flap anastomosis or excision of the posterior flaps?Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007 Jan-Feb;23(1):28-31. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0b013e31802dd766. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. PMID: 17237686 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis of the effect of posterior mucosal flap anastomosis in primary external dacryocystorhinostomy.Clin Ophthalmol. 2013;7:2281-5. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S55508. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24363551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimetabolites as an adjunct to dacryocystorhinostomy for nasolacrimal duct obstruction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 7;4(4):CD012309. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012309.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32259290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caldwell GW. Two new operations for obstruction of the nasal duct, with preservation of the canaliculi, and with an incidental description of a new lacrimal probe. Am J Opthalmol. 1893;10:189–193.
-
- Yuen KSC, Lam LYM, Tse MWY, Chan DDN, Won BWC, Chan WM. Modified endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy with posterior lacrimal sac flap for nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Hong Kong Med J. 2004;10:394–400. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
