Regional Nodal Recurence as a Prognostic Factor in Patients Kept on Observation for cT1-T2 Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Tongue: A Meta-Analysis of 11,973 Patients
- PMID: 37974831
- PMCID: PMC10645994
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04057-w
Regional Nodal Recurence as a Prognostic Factor in Patients Kept on Observation for cT1-T2 Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas of Tongue: A Meta-Analysis of 11,973 Patients
Abstract
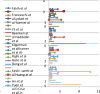
The surgical management of the clinically node negative neck in T1-T2 early oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (OTSCC) has been the topic of debate since few decades. As the occult cervical lymph node metastasis is considered to be the primary prognostic factor in early OTSCC, this meta-analysis has been carried out to find the risk of regional nodal recurrence on patients kept under observation than those who have underwent Elective neck dissection (END). The articles were electronically retrieved from Ovid Medline, PubMed, Cochrane and Scholar for comparison of Observation versus END in early OTSCC. The search strategy identified 35 relevant review articles from April 1979 to April 2020 from different search engines. A total of 11,973 patients from 30 retrospective analyses, 4 prospective and 1 randomized control trials were included in this meta-analysis. Overall test revealed (OR: 13.02 95% CI 1.360-17.154) with t test 2.382 and p value 0.023 which is statistically significant and showed that END significantly reduced the risk of regional nodal recurrence. This meta-analysis finds that there is statistically significant relationship when END was performed which reduced the risk of regional nodal recurrence as seen in patients kept on Observation thereby affecting the Overall survival (OS) rate.
Keywords: Carcinoma tongue; Elective neck dissection; Nodal recurrence; Observation; Prognosis.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global Health Estimates (2016) Deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. Geneva, World Health Organization; 2018; Human Development Report 2016. New York, United Nations Development Programme; 2016
-
- Bagan J, Sarrion G, Jimenez Y. Oral cancer: clinical features. Oral Oncol. 2010;46(414–7):4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous