Wideband Tympanometry (WBT) Features in Children with Cleft Palate and Otitis Media with Effusion Before and After Cleft Palate Surgery
- PMID: 37974839
- PMCID: PMC10646051
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-04059-8
Wideband Tympanometry (WBT) Features in Children with Cleft Palate and Otitis Media with Effusion Before and After Cleft Palate Surgery
Abstract
Aims: In some cases, children with cleft palate undergo unnecessary tympanostomy along with palatoplasty because of inaccurate evaluations in determining the level of otitis media with effusion (OME). Recent studies have shown that wideband tympanometry (WBT) significantly contributes to the accurate evaluation of the middle ear status in children with cleft palate. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate WBT and auditory brainstem response (ABR) indices before and after cleft palate repair surgery.
Materials and methods: The study involved 88 children with cleft palate, and ABR and WBT energy absorbance indices were measured in two phases. The first phase was conducted three months and three days prior to cleft palate repair surgery, and the second phase was carried out one, three, and six months after surgery.
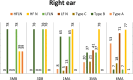
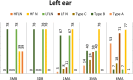
Results: In the first phase, the energy absorbance index of low frequencies was below the normal range in all children, within the normal range at high frequencies in 78 children, and below the normal range in only 10 children three months before cleft palate surgery. In the second phase, the energy absorbance index and hearing thresholds at low frequencies after surgery showed a significant difference compared with the preoperative index (p = 0.001).
Conclusion: Monitoring WBT indices and hearing thresholds in children with cleft palate is effective in determining the appropriate surgery for children with otitis media with effusion (OME). Furthermore, the WBT plays a crucial role in accurately assessing middle ear function after cleft palate surgery.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The clinical value of wideband tympanometry in the diagnosis of otitis media with effusion].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Sep;32(17):1309-1315. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.17.005. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30282184 Chinese.
-
The effect of intervelar veloplasty under magnification (Sommerlad's Technique) without tympanostomy on middle ear effusion in cleft palate patients.BMC Pediatr. 2021 Sep 1;21(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02856-0. BMC Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34470606 Free PMC article.
-
[Characteristics of secretory otitis media in children with cleft palate and timing of intervention of tympanic membrane].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jul;33(7):647-650. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.07.017. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31327205 Chinese.
-
Managing Chronic otitis media with Effusion in Children with non-Syndromic Cleft Palate: Short-Term Ventilation Tubes Versus Surveillance.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2024 Jun;61(6):905-916. doi: 10.1177/10556656221148368. Epub 2023 Jan 4. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2024. PMID: 36600676
-
Otitis media with effusion in children with cleft lip and palate: a narrative review.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Sep;77(9):1403-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.07.015. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23931986 Review.
References
-
- Coleman J, Jr, Sykes J. The embryology, classification, epidemiology, and genetics of facial clefting. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2001;9(1):1–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
