Lateral Stenosis of External Auditory Canal Secondary to Corrosive acid Injury: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature
- PMID: 37974851
- PMCID: PMC10645683
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-023-03941-9
Lateral Stenosis of External Auditory Canal Secondary to Corrosive acid Injury: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
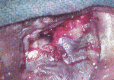
Acquired external auditory canal (EAC) stenosis is an uncommon condition with an incidence of 0.6 in 100,000 population. Road traffic accidents and otology surgeries are the frequently reported causes for it to occur. The high rate of restenosis makes this condition difficult to manage. A 50 year old lady presented with history of accidental instillation of acid in her left ear at 6 months of age by the care giver. The patient developed stenosis of left EAC with hearing loss. Examination revealed pin point stenosis of left EAC. Puretone audiogram revealed a moderately severe conductive hearing loss. Computed tomogram showed soft tissue lesion obliterating the entire EAC and extending into the middle ear and antrum. Intra operatively only the cartilaginous EAC was stenosed. Surgical excision of the fibrotic scar with a tympanomastoidectomy and wide meatoplasty was done. Regular post operative aural toileting, packing with merocele strips and application of topical antibiotic -steroid preparations was done. 6 months post-surgery a patent EAC and healed tympanic membrane was achieved. In this report, we present a rare case of lateral EAC stenosis secondary to corrosive acid injury, highlighting the surgical steps, post operative care and surgical outcomes. A limited review of literature is also presented.
Keywords: Corrosive acid injury; Excision; External auditory canal; Stenosis; Stents; Surgery; Tympanomastoidectomy.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Rare Case of Post Inflammatory Lateral Stenosis of External Auditory Canal and It's Management with Review of Literature.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Aug;74(Suppl 1):437-441. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02203-2. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36032897 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired medial external auditory canal stenosis, anterior tympanomeatal angle blunting, and lateralized tympanic membrane: Nosology, diagnosis, and treatment.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2019 Apr;136(2):93-97. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2018.12.002. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2019. PMID: 30639598
-
Morphological characteristics of external auditory canal in congenital aural stenosis patients.Am J Otolaryngol. 2017 Jul-Aug;38(4):422-427. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28390808
-
Acquired Stenosis of the External Ear Canal.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2023 Oct;56(5):919-931. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2023.06.012. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 37553271 Review.
-
Hemangioma of the External Auditory Canal and Temporal Bone: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review.Ear Nose Throat J. 2024 Dec;103(12):NP720-NP726. doi: 10.1177/01455613211029795. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Ear Nose Throat J. 2024. PMID: 35354340 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
