The potential protective effect of aqueous extract of Acanthophyllum glandulosum root on Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice
- PMID: 37975083
- PMCID: PMC10638328
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-023-01238-w
The potential protective effect of aqueous extract of Acanthophyllum glandulosum root on Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice
Abstract
Purpose: Treatment of diabetes using traditional medicine has attracted attention in recent decades because of its unique benefits. Acanthophyllum glandulosum is known as an herb with therapeutic potential. This research explored the likely protective effects of Acanthophyllum Glandulosum Root (AGR) in mice with Streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) to provide complementary therapy.
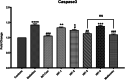
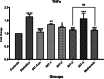
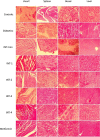
Methods: Diabetes was induced by a single injection of Streptozotocin (STZ) in mice. STZ-diabetic mice were treated with oral dosages of AGR (25, 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg) on different experiment days. During the experiment, the effect of a topical extract of AGR on Glucose level, serum lipid profile, and liver and kidney biomarkers, with the histopathological assessment of heart, kidney, spleen, and liver, were investigated. The gene expression level of inflammation biomarkers (Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 (IL-1)), apoptosis factor (Caspase3), glucose regulatory genes (Glucose transporter (GLUT) 4 and 2), and lipid regulatory gene (Adenosine 50-monophosphate protein-kinase (AMPK)) were investigated.
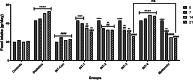
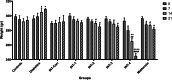
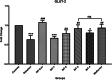
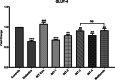
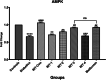
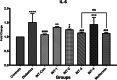
Results: Administration of AGR to STZ-diabetic mice decreased blood glucose level (p < 0.01), normalized the lipid profile (p < 0.01), improved the serum level of kidney (p < 0.01) and liver biomarkers (p < 0.01), and normalized Kidney hypertrophy (p < 0.01), inflammation (p < 0.001), and apoptosis (p < 0.01). The AGR effect was better at 100 mg/kg than Metformin (100 mg/kg) on healing T2DM condition in mice.
Conclusion: AGR possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-glycation activity, thus exhibiting a protective function in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Further in vitro and in vivo works are necessary, especially to elucidate the mechanism of action of AGR at the cellular and molecular levels.
Keywords: Acanthophyllum glandulosum root; Apoptosis; Diabetes Mellitus; Glucose; Inflammation; Lipid Metabolism.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestThe authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
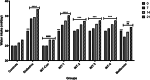
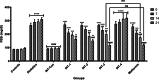
References
-
- Suryasa IW, et al. Health and treatment of diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Health Sciences. 2021;5(1):1–5.
-
- Lestari L, et al. Diabetes Melitus: Review etiologi, patofisiologi, gejala, penyebab, cara pemeriksaan, cara pengobatan dan cara pencegahan. InProsiding Seminar Nasional Biologi. 2021;7(1):237–241.
-
- Standl E et al. The global epidemics of diabetes in the 21st century: Current situation and perspectives. Eur J Prevent Cardiol. 2019;26(2_suppl):7–14. - PubMed
-
- Eizirik DL, Pasquali L, Cnop M. Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: different pathways to failure. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(7):349–362. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

