Effects of resistance training on muscular strength, endurance, body composition and functional performance among sarcopenic patients: a systematic review
- PMID: 37975091
- PMCID: PMC10638274
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-023-01283-5
Effects of resistance training on muscular strength, endurance, body composition and functional performance among sarcopenic patients: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenia, a gradual loss of muscle mass and strength associated with ageing, contributes to a decline in physical abilities, increase in disability and frailty and loss of functional independence. This functional deterioration which comes with ageing, can be slowed in pace with exercise.
Objective: The objective of the current review was to thoroughly search for literature assessing impact of RT on physical performance, body composition, muscle strength and endurance in sarcopenic elderly patients.
Methods: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and PEDro databases were brought in use for a thorough search for articles published from 2010 to 2023. Two researchers independently retrieved data from studies that complied with the inclusion and exclusion criteria, while they also evaluated quality of the evidence.
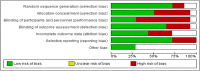
Results: In total, 14 studies with 742 patients with mean age of 72.4 ± 9.22 years were included in the analysis for this review. Results indicate, RT improves body composition (p = 0.001), functional performance (p 0.001), postural stability (p = 0.005) and muscle strength (p 0.001) in elderly sarcopenic patients.
Conclusion: A promising intervention for the management of sarcopenia is RT. To yield RT's positive effects, a well-designed prescription is the need of the hour, just like it is with other treatment strategies.
Keywords: Ageing; Body composition; Frailty; Sarcopenia.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of different exercise training modes on muscle strength and physical performance in older people with sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Geriatr. 2021 Dec 15;21(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02642-8. BMC Geriatr. 2021. PMID: 34911483 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Different Exercise Training Types on Body Composition and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Nutr Health Aging. 2023;27(11):1076-1090. doi: 10.1007/s12603-023-2018-6. J Nutr Health Aging. 2023. PMID: 37997730
-
Benefits of Resistance Training in Early and Late Stages of Frailty and Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 12;10(8):1630. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081630. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33921356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Physical Exercise Programs on Sarcopenia Management, Dynapenia, and Physical Performance in the Elderly: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.J Aging Res. 2019 Nov 20;2019:1959486. doi: 10.1155/2019/1959486. eCollection 2019. J Aging Res. 2019. PMID: 31827927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Resistance Training on Muscular Fitness, Muscle Morphology, and Body Composition in Elite Female Athletes: A Systematic Review.Sports Med. 2023 Sep;53(9):1709-1735. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01859-4. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37289331 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of muscle fatigability using isometric repetitive handgrip strength in frail older adults. A cross-sectional study.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 21;23(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06239-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39985087 Free PMC article.
-
A 4-Week Mobile App-Based Telerehabilitation Program vs Conventional In-Person Rehabilitation in Older Adults With Sarcopenia: Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jan 24;27:e67846. doi: 10.2196/67846. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 39854716 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Resistance exercise training in older men reduces ATF4-activated and senescence-associated mRNAs in skeletal muscle.Geroscience. 2025 Jun;47(3):4601-4622. doi: 10.1007/s11357-025-01564-2. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 40011348 Free PMC article.
-
The Valemee Visual System Helps Reduce Risk for Chronic Illness by Promoting Physical Fitness, Self-Efficacy and Independence in Adults With Intellectual Disabilities.J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025 Jan;38(1):e70011. doi: 10.1111/jar.70011. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025. PMID: 39806547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang K-V, Hsu T-H, Wu W-T, Huang K-C, Han D-S. Association between sarcopenia and cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2016;17:1164.e7–1164.e15. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

