A comprehensive review on the risks assessment and treatment options for Sarcopenia in people with diabetes
- PMID: 37975099
- PMCID: PMC10638272
- DOI: 10.1007/s40200-023-01262-w
A comprehensive review on the risks assessment and treatment options for Sarcopenia in people with diabetes
Abstract
Objectives: This comprehensive review aims to examine the reciprocal interplay between Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and sarcopenia, identify prevailing research gaps, and discuss therapeutic approaches and measures to enhance healthcare practices within hospital settings.
Methods: A thorough literature review was conducted to gather relevant studies and articles on the relationship between T2DM and sarcopenia. Various databases were searched, including Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, and Science Direct databases. The search terms included T2DM, sarcopenia, inflammation, insulin resistance, advanced glycation end products, oxidative stress, muscle dimensions, muscle strength, muscle performance, aging, nutrition, hormone levels, and physical activity. The collected articles were critically analysed to extract key findings and identify gaps in current research.
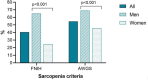
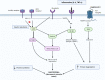
Results: The prevalence and incidence of metabolic and musculoskeletal disorders, notably T2DM and sarcopenia, have surged in recent years. T2DM is marked by inflammation, insulin resistance, accumulation of advanced glycation end products, and oxidative stress, while sarcopenia involves a progressive decline in skeletal muscle mass and function. The review underscores the age-related correlation between sarcopenia and adverse outcomes like fractures, falls, and mortality. Research gaps regarding optimal nutritional interventions for individuals with T2DM and sarcopenia are identified, emphasizing the necessity for further investigation in this area.
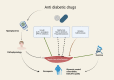
Conclusions: The reciprocal interplay between T2DM and sarcopenia holds significant importance. Further research is warranted to address knowledge gaps, particularly in utilizing precise measurement tools during clinical trials. Lifestyle modifications appear beneficial for individuals with T2DM and sarcopenia. Additionally, practical nutritional interventions require investigation to optimize healthcare practices in hospital settings.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40200-023-01262-w.
Keywords: Health metabolic health; Muscle; Obesity; Sarcopenia; T2DM.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Tehran University of Medical Sciences 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
This paper is devoid of any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sarcopenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a bidirectional relationship.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019 Jul 8;12:1057-1072. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S186600. eCollection 2019. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2019. PMID: 31372016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcopenia and Chronic Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Rev Diabet Stud. 2022 Sep 28;18(3):157-165. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2022.18.157. Rev Diabet Stud. 2022. PMID: 36309772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Association Between Sarcopenia and Diabetes: From Pathophysiology Mechanism to Therapeutic Strategy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 May 30;16:1541-1554. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S410834. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37275941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of sarcopenia pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches: resistance exercise, nutrition, and monoterpenes.Phys Act Nutr. 2024 Dec;28(4):83-91. doi: 10.20463/pan.2024.0036. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Phys Act Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39934634 Free PMC article.
-
The risks of sarcopenia, falls and fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Maturitas. 2018 Mar;109:70-77. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.12.011. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Maturitas. 2018. PMID: 29452785 Review.
Cited by
-
Knee proprioception, muscle strength, and stability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus- A cross-sectional study.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39270. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39270. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498014 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Nutrition Therapy and Physical Exercise for Acute and Chronic Hyperglycemic Patients with Sarcopenia.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 29;17(3):499. doi: 10.3390/nu17030499. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin angiotensin system-induced muscle wasting: putative mechanisms and implications for clinicians.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):1935-1949. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05043-8. Epub 2024 May 29. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38811433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Musumeci G. Sarcopenia and Exercise “The state of the art. J Funct Morphology Kinesiol. 2017;2(4):40.
-
- UN. United Nations. Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division: World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Table 2017; (accessed on 25 September 2019).
-
- Pal R, Aggarwal A, Singh T, Sharma S, Khandelwal N, Garg A, Bhansali A, Kumar A, Yadav U, Singh P, Dhiman V, Dutta P, Bhadada SK. Diagnostic cut-offs, prevalence, and biochemical predictors of sarcopenia in healthy indian adults: the Sarcopenia-Chandigarh Urban Bone Epidemiological Study (Sarco-CUBES). Eur Geriatr Med. 2020 Oct;11(5):725–36. - PubMed
-
- Kapoor D, Piplani T, Singh A, Perwaiz A, Chaudhary A. Defining Sarcopenia in the indian Population—a step Forward. Indian J Surg. 2021;83(2):476–82.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

