A novel nomogram based on body composition and nutritional indicators to predict the prognosis of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy
- PMID: 37975152
- PMCID: PMC10757150
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.6712
A novel nomogram based on body composition and nutritional indicators to predict the prognosis of patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prognostic significance of body composition and nutritional indicators in patients undergoing radical cystectomy with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and to develop a novel nomogram that accurately predicts overall survival (OS).
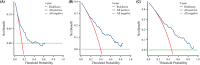
Methods: From December 2010 to December 2020, we retrospectively collected clinical and pathological data from 373 MIBC patients who underwent radical cystectomy at our hospital. Preoperative computed tomography (CT) images were used to measure the skeletal muscle index (SMI), subcutaneous adipose index (SAI), visceral adipose index (VAI), skeletal muscle density (SMD), subcutaneous adipose density (SAD), visceral adipose density (VAD), and visceral adipose to subcutaneous adipose area ratio (VSR). The clinicopathological characteristics were evaluated using LASSO regression and multivariate Cox regression, and a nomogram was constructed to predict 1-, 3-, and 5-year overall survival. The concordance index (C-index), time-dependent receiver operating characteristic curves (t-ROC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA) were used to assess the discriminative ability, calibration, and clinical practicality of the nomogram.
Results: Multivariate analyses demonstrated that pT stage, lymph node status, LVI, SMD, and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) are independent prognostic factors for OS. Additionally, a nomogram was created. The nomogram's C-index was 0.714 (95% CI: 0.695-0.733). The area under the t-ROC curve of 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival corresponding to the model was 0.726, 0.788, and 0.785, respectively. The calibration curve demonstrated excellent agreement between the predicted and observed outcomes. The DCA revealed that patients with MIBC could benefit from the nomogram.
Conclusion: Based on body composition and nutritional indicators, we developed a novel nomogram with excellent predictive accuracy and reliability for predicting the prognosis of MIBC patients undergoing RC.
Keywords: MIBC; body composition; nomogram; nutritional indicators; prognosis.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests disclosed by the authors.
Figures







References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on non‐muscle‐invasive bladder cancer (Ta, T1, and carcinoma in situ). Eur Urol. 2021;81:75‐94. - PubMed
-
- Witjes JA, Bruins HM, Cathomas R, et al. European Association of Urology guidelines on muscle‐invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur Urol. 2021;79(1):82‐104. - PubMed
-
- Arcangeli G, Strigari L, Arcangeli S. Radical cystectomy versus organ‐sparing trimodality treatment in muscle‐invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review of clinical trials. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;95(3):387‐396. - PubMed
-
- Ghoneim MA, Abdel‐Latif M, el‐Mekresh M, et al. Radical cystectomy for carcinoma of the bladder: 2,720 consecutive cases 5 years later. J Urol. 2008;180(1):121‐127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

