Gene communities in co-expression networks across different tissues
- PMID: 37976327
- PMCID: PMC10691702
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011616
Gene communities in co-expression networks across different tissues
Abstract
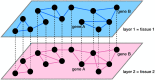
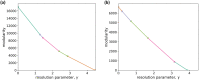
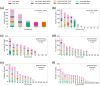
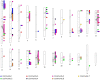
With the recent availability of tissue-specific gene expression data, e.g., provided by the GTEx Consortium, there is interest in comparing gene co-expression patterns across tissues. One promising approach to this problem is to use a multilayer network analysis framework and perform multilayer community detection. Communities in gene co-expression networks reveal groups of genes similarly expressed across individuals, potentially involved in related biological processes responding to specific environmental stimuli or sharing common regulatory variations. We construct a multilayer network in which each of the four layers is an exocrine gland tissue-specific gene co-expression network. We develop methods for multilayer community detection with correlation matrix input and an appropriate null model. Our correlation matrix input method identifies five groups of genes that are similarly co-expressed in multiple tissues (a community that spans multiple layers, which we call a generalist community) and two groups of genes that are co-expressed in just one tissue (a community that lies primarily within just one layer, which we call a specialist community). We further found gene co-expression communities where the genes physically cluster across the genome significantly more than expected by chance (on chromosomes 1 and 11). This clustering hints at underlying regulatory elements determining similar expression patterns across individuals and cell types. We suggest that KRTAP3-1, KRTAP3-3, and KRTAP3-5 share regulatory elements in skin and pancreas. Furthermore, we find that CELA3A and CELA3B share associated expression quantitative trait loci in the pancreas. The results indicate that our multilayer community detection method for correlation matrix input extracts biologically interesting communities of genes.
Copyright: © 2023 Russell et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Update of
-
Gene communities in co-expression networks across different tissues.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 7:arXiv:2305.12963v2. ArXiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Nov 17;19(11):e1011616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011616. PMID: 37292479 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Gene communities in co-expression networks across different tissues.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 7:arXiv:2305.12963v2. ArXiv. 2023. Update in: PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Nov 17;19(11):e1011616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011616. PMID: 37292479 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Exploring regulation in tissues with eQTL networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Sep 12;114(37):E7841-E7850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707375114. Epub 2017 Aug 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28851834 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-Tissue Gene Co-Expression Networks between Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Individuals.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167519. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907186 Free PMC article.
-
An expression quantitative trait loci-guided co-expression analysis for constructing regulatory network using a rice recombinant inbred line population.J Exp Bot. 2014 Mar;65(4):1069-79. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert464. Epub 2014 Jan 13. J Exp Bot. 2014. PMID: 24420573 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayer modelling of the human transcriptome and biological mechanisms of complex diseases and traits.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2021 May 27;7(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s41540-021-00186-6. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 34045472 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uremic toxin receptor NR1H3 contributes to hyperlipidemia- and chronic kidney disease-accelerated vascular inflammation, which is partially suppressed by novel YBX2 anti-ROS pathway.Redox Biol. 2025 Sep;85:103724. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103724. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40505347 Free PMC article.
-
Switch-like Gene Expression Modulates Disease Susceptibility.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 13:rs.3.rs-4974188. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4974188/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 18;16(1):5323. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60513-x. PMID: 39315271 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Switch-like Gene Expression Modulates Disease Susceptibility.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 25:2024.08.24.609537. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.24.609537. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 18;16(1):5323. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60513-x. PMID: 39229158 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Introduction to correlation networks: Interdisciplinary approaches beyond thresholding.Phys Rep. 2025 Aug 21;1136:1-39. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2025.06.002. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Phys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40814354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fortunato S. Community detection in graphs. Phys Rep. 2010;486(3-5):75–174. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2009.11.002 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

