LRH-1 agonist DLPC through STAT6 promotes macrophage polarization and prevents parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in mice
- PMID: 37976384
- PMCID: PMC11023811
- DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000690
LRH-1 agonist DLPC through STAT6 promotes macrophage polarization and prevents parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in mice
Abstract
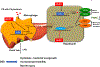
Background and aims: Parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis (PNAC) is an important complication in patients with intestinal failure with reduced LRH-1 expression. Here, we hypothesized that LRH-1 activation by its agonist, dilauroylphosphatidylcholine (DLPC), would trigger signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) signaling and hepatic macrophage polarization that would mediate hepatic protection in PNAC.
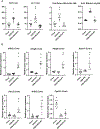
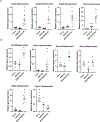
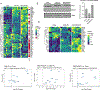
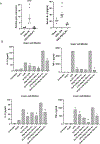
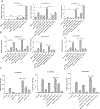
Approach and results: PNAC mouse model (oral DSSx4d followed by PNx14d; DSS-PN) was treated with LRH-1 agonist DLPC (30 mg/kg/day) intravenously. DLPC treatment prevented liver injury and cholestasis while inducing hepatic mRNA expression of Nr5a2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2), Abcb11 (ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 11), Abcg5 (ATP-binding cassette [ABC] transporters subfamily G member 5), Abcg8 (ATP-binding cassette [ABC] transporters subfamily G member 8), nuclear receptor subfamily 0, and ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 2 ( Abcc2) mRNA, all of which were reduced in PNAC mice. To determine the mechanism of the DLPC effect, we performed RNA-sequencing analysis of the liver from Chow, DSS-PN, and DSS-PN/DLPC mice, which revealed DLPC upregulation of the anti-inflammatory STAT6 pathway. In intrahepatic mononuclear cells or bone-marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) from PNAC mice, DLPC treatment prevented upregulation of pro-inflammatory (M1) genes, suppressed activation of NFκB and induced phosphorylation of STAT6 and its target genes, indicating M2 macrophage polarization. In vitro, incubation of DLPC with cultured macrophages showed that the increased Il-1b and Tnf induced by exposure to lipopolysaccharides or phytosterols was reduced significantly, which was associated with increased STAT6 binding to promoters of its target genes. Suppression of STAT6 expression by siRNA in THP-1 cells exposed to lipopolysaccharides, phytosterols, or both resulted in enhanced elevation of IL-1B mRNA expression. Furthermore, the protective effect of DLPC in THP-1 cells was abrogated by STAT6 siRNA.
Conclusions: These results indicate that activation of LRH-1 by DLPC may protect from PNAC liver injury through STAT6-mediated macrophage polarization.
Copyright © 2023 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








Similar articles
-
NF-κB Regulation of LRH-1 and ABCG5/8 Potentiates Phytosterol Role in the Pathogenesis of Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Cholestasis.Hepatology. 2021 Dec;74(6):3284-3300. doi: 10.1002/hep.32071. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34310734 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic activation of hepatic farnesoid X receptor prevents parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in mice.Hepatology. 2022 Feb;75(2):252-265. doi: 10.1002/hep.32101. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 34387888
-
Macrophage-derived IL-1β/NF-κB signaling mediates parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 11;9(1):1393. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03764-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29643332 Free PMC article.
-
Association of ABCG5 and ABCG8 Transporters with Sitosterolemia.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1440:31-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43883-7_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38036873 Review.
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Protein Regulators of Cholesterol Homeostasis in Immune Modulation and Cancer Pathophysiology.Endocrinology. 2025 Feb 27;166(4):bqaf031. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf031. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 39951497 Review.
-
Impact of Heat Stress on Gene Expression in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian Axis of Hu Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 25;15(15):2189. doi: 10.3390/ani15152189. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804979 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis and Management of Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2025 Mar;45(1):66-80. doi: 10.1055/a-2545-7370. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Semin Liver Dis. 2025. PMID: 40015320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of gut hormones.Mol Cells. 2024 Nov;47(11):100126. doi: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100126. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Mol Cells. 2024. PMID: 39426686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- El Kasmi KC, Ghosh S, Anderson AL, Devereaux MW, Balasubramaniyan N, D’Alessandro A, Orlicky DJ, et al. Pharmacologic activation of hepatic farnesoid X receptor prevents parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis in mice. Hepatology 2022;75:252–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

