Characterization of neural damage and neuroinflammation in Pax6 small-eye mice
- PMID: 37979905
- PMCID: PMC10843716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109723
Characterization of neural damage and neuroinflammation in Pax6 small-eye mice
Abstract
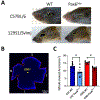
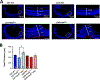
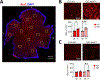
Aniridia is a panocular condition characterized by a partial or complete loss of the iris. It manifests various developmental deficits in both the anterior and posterior segments of the eye, leading to a progressive vision loss. The homeobox gene PAX6 plays an important role in ocular development and mutations of PAX6 have been the main causative factors for aniridia. In this study, we assessed how Pax6-haploinsufficiency affects retinal morphology and vision of Pax6Sey mice using in vivo and ex vivo metrics. We used mice of C57BL/6 and 129S1/Svlmj genetic backgrounds to examine the variable severity of symptoms as reflected in human aniridia patients. Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) was observed in Pax6Sey mice starting from post-natal day 20 (P20). Correspondingly, visual acuity showed a steady age-dependent decline in Pax6Sey mice, though these phenotypes were less severe in the 129S1/Svlmj mice. Local retinal damage with layer disorganization was assessed at P30 and P80 in the Pax6Sey mice. Interestingly, we also observed a greater number of activated Iba1+ microglia and GFAP + astrocytes in the Pax6Sey mice than in littermate controls, suggesting a possible neuroinflammatory response to Pax6 deficiencies.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None.
Figures



References
-
- Beckmann L, Cai Z, Cole J, Miller DA, Liu M, Grannonico M, Zhang X, Ryu HJ, Netland PA, Liu X, Zhang HF, 2021. In vivo imaging of the inner retinal layer structure in mice after eye-opening using visible-light optical coherence tomography. Exp Eye Res 211, 108756. 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108756 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhan A, Browning AC, Shah S, Hamilton R, Dave D, Dua HS, 2002. Effect of corneal thickness on intraocular pressure measurements with the pneumotonometer, Goldmann applanation tonometer, and Tono-Pen. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43, 1389–1392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

