Updates in NMOSD and MOGAD Diagnosis and Treatment: A Tale of Two Central Nervous System Autoimmune Inflammatory Disorders
- PMID: 37980124
- PMCID: PMC10658081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2023.06.009
Updates in NMOSD and MOGAD Diagnosis and Treatment: A Tale of Two Central Nervous System Autoimmune Inflammatory Disorders
Abstract
Aquaporin-4-IgG positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (AQP4+NMOSD) and myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease (MOGAD) are antibody-associated diseases targeting astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, respectively. Their recognition as distinct entities has led to each having its own diagnostic criteria that require a combination of clinical, serologic, and MRI features. The therapeutic approach to acute attacks in AQP4+NMOSD and MOGAD is similar. There is now class 1 evidence to support attack-prevention medications for AQP4+NMOSD. MOGAD lacks proven treatments although clinical trials are now underway. In this review, we will outline similarities and differences between AQP4+NMOSD and MOGAD in terms of diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: AQP4-IgG; Diagnosis; MOG; MOG-IgG; Treatment; aquaporin-4; myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

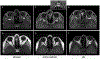
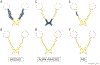


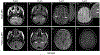

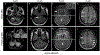
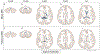

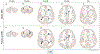
References
-
- Banwell B, Bennett JL, Marignier R, et al. Diagnosis of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease: International MOGAD Panel proposed criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(3):268–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

