Health Equity Impact Assessment (HEIA) reporting tool: developing a checklist for policymakers
- PMID: 37980523
- PMCID: PMC10657117
- DOI: 10.1186/s12939-023-02031-0
Health Equity Impact Assessment (HEIA) reporting tool: developing a checklist for policymakers
Abstract
Introduction: Health Equity Impact Assessment (HEIA) is a decision support tool that shows users how a new program, policy, or innovation affects health equity in different population groups. Various HEIA reporting and dissemination tools are available, nevertheless, a practical standard tool to present the results of HEIA in an appropriate period to policymakers is lacking. This work reports the development of a tool (a checklist) for HEIA reporting at the decision-making level, aiming to promote the application of HEIA evidence for improving health equity.
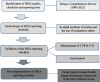
Methods: This is a mixed-method study that was carried out over four stages in 2022-2023: 1) identifying HEIA models, checklists, and reporting instruments; 2) development of the initial HEIA reporting checklist; 3) checklist validation; and 4) piloting the checklist. We also analyzed the Face, CVR, and CVI validity of the tool.
Results: We developed the initial checklist through analysis of 53 included studies and the opinions of experts. The final checklist comprised five sections: policy introduction (eight subsections), managing the HEIA of policy (seven subsections), scope of the affected population (three subsections), HEIA results (seven subsections), and recommendations (three subsections).
Conclusion: Needs assessment, monitoring during implementation, health impact assessment, and other tools such as monitoring outcome reports, appraisals, and checklists are all methods for assessing health equity impact. Other equity-focused indicators, such as the equity lens and equity appraisal, may have slightly different goals than the HEIA. Similarly, the formats for presenting and publishing HEIA reports might vary, depending on the target population and the importance of the report.
Keywords: Health Equity; Health Equity Impact Assessment (HEIA); Health Impact Assessment (HIA); Health Policy; Inequality in health.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HEIA tools: inclusion of migrants in health policy in Canada.Health Promot Int. 2019 Aug 1;34(4):697-705. doi: 10.1093/heapro/day016. Health Promot Int. 2019. PMID: 29672682
-
Implementation of the Health Equity Impact Assessment (HEIA) tool in a local public health setting: challenges, facilitators, and impacts.Can J Public Health. 2020 Apr;111(2):212-219. doi: 10.17269/s41997-019-00269-2. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Can J Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31755052 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Health Equity Impact Assessment 'Indigenous Lens Tool' to address challenges in providing equitable cancer screening for indigenous peoples.BMC Public Health. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):2250. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16919-7. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37968666 Free PMC article.
-
Health Impact Assessment of Transportation Projects and Policies: Living Up to Aims of Advancing Population Health and Health Equity?Annu Rev Public Health. 2019 Apr 1;40:305-318. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040617-013836. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Annu Rev Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30601724 Review.
-
Representations of clinical practice guidelines and health equity in healthcare literature: An integrative review.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2023 Mar;55(2):506-520. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12847. Epub 2022 Nov 23. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2023. PMID: 36419399 Review.
Cited by
-
Applying the principle of justice in digital health.NPJ Digit Med. 2025 Jul 21;8(1):467. doi: 10.1038/s41746-025-01877-8. NPJ Digit Med. 2025. PMID: 40691313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to optimise the health equity impact of digital pain self-reporting tools: a series of multi-stakeholder focus groups.Int J Equity Health. 2024 Nov 11;23(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12939-024-02299-w. Int J Equity Health. 2024. PMID: 39529006 Free PMC article.
-
How to design equitable digital health tools: A narrative review of design tactics, case studies, and opportunities.PLOS Digit Health. 2024 Aug 22;3(8):e0000591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000591. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLOS Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39172776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health equity checklist for research.Ethics Med Public Health. 2025;33:101064. doi: 10.1016/j.jemep.2025.101064. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Ethics Med Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40585904 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gaps and opportunities for measuring equity with the Translational Science Benefits Model: Recommendations from the Center for American Indian and Alaska Native Diabetes Translation Research.J Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Oct 24;8(1):e206. doi: 10.1017/cts.2024.638. eCollection 2024. J Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39655025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bond A, Cave B, Ballantyne R. Who plans for health improvement? SEA, HIA and the separation of spatial planning and health planning. Environ Impact Assess Rev. 2013;42:67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2012.10.002. - DOI
-
- Organization WH . Universal health coverage. 2013.
-
- Lozano R, Fullman N, Mumford JE, Knight M, Barthelemy CM, Abbafati C, et al. Measuring universal health coverage based on an index of effective coverage of health services in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1250–1284. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30750-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haakenstad A, Irvine CMS, Knight M, Bintz C, Aravkin AY, Zheng P, et al. Measuring the availability of human resources for health and its relationship to universal health coverage for 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2022;399(10341):2129–2154. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00532-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Abbas KM, Abbasifard M, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1160–1203. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30977-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources