Genome-wide profiling of transcription factor activity in primary liver cancer using single-cell ATAC sequencing
- PMID: 37980571
- PMCID: PMC10750269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113446
Genome-wide profiling of transcription factor activity in primary liver cancer using single-cell ATAC sequencing
Abstract
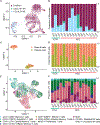
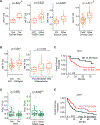
Primary liver cancer (PLC) consists of two main histological subtypes; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA). The role of transcription factors (TFs) in malignant hepatobiliary lineage commitment between HCC and iCCA remains underexplored. Here, we present genome-wide profiling of transcription regulatory elements of 16 PLC patients using single-cell assay for transposase accessible chromatin sequencing. Single-cell open chromatin profiles reflect the compositional diversity of liver cancer, identifying both malignant and microenvironment component cells. TF motif enrichment levels of 31 TFs strongly discriminate HCC from iCCA tumors. These TFs are members of the nuclear/retinoid receptor, POU, or ETS motif families. POU factors are associated with prognostic features in iCCA. Overall, nuclear receptors, ETS and POU TF motif families delineate transcription regulation between HCC and iCCA tumors, which may be relevant to development and selection of PLC subtype-specific therapeutics.
Keywords: CP: Cancer; ETS; POU; hepatocellular carcinoma; intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; nuclear receptors; primary liver cancer; retinoid receptors; scATAC-seq; transcription factor.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

