Cell and biomaterial delivery strategies to induce immune tolerance
- PMID: 37980950
- PMCID: PMC10842132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115141
Cell and biomaterial delivery strategies to induce immune tolerance
Abstract
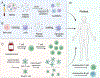
The prevalence of immune-mediated disorders, including autoimmune conditions and allergies, is steadily increasing. However, current therapeutic approaches are often non-specific and do not address the underlying pathogenic condition, often resulting in impaired immunity and a state of generalized immunosuppression. The emergence of technologies capable of selectively inhibiting aberrant immune activation in a targeted, antigen (Ag)-specific manner by exploiting the body's intrinsic tolerance pathways, all without inducing adverse side effects, holds significant promise to enhance patient outcomes. In this review, we will describe the body's natural mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance as well as innovative delivery strategies using cells and biomaterials targeting innate and adaptive immune cells to promote Ag-specific immune tolerance. Additionally, we will discuss the challenges and future opportunities that warrant consideration as we navigate the path toward clinical implementation of tolerogenic strategies to treat immune-mediated diseases.
Keywords: Adaptive immune responses; Adoptive cell therapies; Antigen delivery systems; Autoimmune diseases; Immune tolerance; Innate immune response; Nanoparticles.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
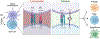
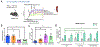

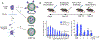
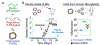
References
-
- Wood RA, Camargo CA, Lieberman P, Sampson HA, Schwartz LB, Zitt M, Collins C, Tringale M, Wilkinson M, Boyle J, Simons FER, Anaphylaxis in America: The prevalence and characteristics of anaphylaxis in the United States, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 133 (2014) 461–467. 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Wang F, Gershwin ME, Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update, J Intern Med. 278 (2015) 369–395. - PubMed
-
- Lapadula G, Marchesoni A, Armuzzi A, Blandizzi C, Caporali R, Chimenti S, Cimaz R, Cimino L, Gionchetti P, Girolomoni G, Lionetti P, Marcellusi A, Mennini FS, Salvarani C, Adalimumab in the treatment of immune-mediated diseases., Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 27 (2014) 33–48. 10.1177/03946320140270S103. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

