Mass Spectrometric Analysis of the Active Site Tryptic Peptide of Recombinant O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Following Incubation with Human Colorectal DNA Reveals the Presence of an O6-Alkylguanine Adductome
- PMID: 37983188
- PMCID: PMC10731659
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00207
Mass Spectrometric Analysis of the Active Site Tryptic Peptide of Recombinant O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Following Incubation with Human Colorectal DNA Reveals the Presence of an O6-Alkylguanine Adductome
Abstract
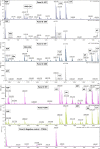
Human exposure to DNA alkylating agents is poorly characterized, partly because only a limited range of specific alkyl DNA adducts have been quantified. The human DNA repair protein, O6-methylguanine O6-methyltransferase (MGMT), irreversibly transfers the alkyl group from DNA O6-alkylguanines (O6-alkGs) to an acceptor cysteine, allowing the simultaneous detection of multiple O6-alkG modifications in DNA by mass spectrometric analysis of the MGMT active site peptide (ASP). Recombinant MGMT was incubated with oligodeoxyribonucleotides (ODNs) containing different O6-alkGs, Temozolomide-methylated calf thymus DNA (Me-CT-DNA), or human colorectal DNA of known O6-MethylG (O6-MeG) levels. It was digested with trypsin, and ASPs were detected and quantified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. ASPs containing S-methyl, S-ethyl, S-propyl, S-hydroxyethyl, S-carboxymethyl, S-benzyl, and S-pyridyloxobutyl cysteine groups were detected by incubating MGMT with ODNs containing the corresponding O6-alkGs. The LOQ of ASPs containing S-methylcysteine detected after MGMT incubation with Me-CT-DNA was <0.05 pmol O6-MeG per mg CT-DNA. Incubation of MGMT with human colorectal DNA produced ASPs containing S-methylcysteine at levels that correlated with those of O6-MeG determined previously by HPLC-radioimmunoassay (r2 = 0.74; p = 0.014). O6-CMG, a putative O6-hydroxyethylG adduct, and other potential unidentified MGMT substrates were also detected in human DNA samples. This novel approach to the identification and quantitation of O6-alkGs in human DNA has revealed the existence of a human DNA alkyl adductome that remains to be fully characterized. The methodology establishes a platform for characterizing the human DNA O6-alkG adductome and, given the mutagenic potential of O6-alkGs, can provide mechanistic information about cancer pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lijinsky W.Chemistry and biology of N-nitroso compounds; Cambridge Monographs on Cancer Research, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1992.
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer . Review of Human Carcinogens; IARC Monograph: Lyon France, 2012. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol100E/mono100E-9.pdf.
-
- Gurjao C.; Zhong R.; Haruki K.; Li Y. Y.; Spurr L. F.; Lee-Six H.; et al. Discovery and Features of an Alkylating Signature in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discovery 2021, 11, 2446–2455. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1656. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

