Neonatal sepsis as a cause of retinopathy of prematurity: An etiological explanation
- PMID: 37984792
- PMCID: PMC10842718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2023.101230
Neonatal sepsis as a cause of retinopathy of prematurity: An etiological explanation
Abstract
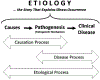
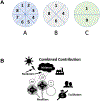
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a complex neonatal disorder with multiple contributing factors. In this paper we have mounted the evidence in support of the proposal that neonatal sepsis meets all requirements for being a cause of ROP (not a condition, mechanism, or even innocent bystander) by means of initiating the early stages of the pathomechanism of ROP occurrence, systemic inflammation. We use the model of etiological explanation, which distinguishes between two overlapping processes in ROP causation. It can be shown that sepsis can initiate the early stages of the pathomechanism via systemic inflammation (causation process) and that systemic inflammation can contribute to growth factor aberrations and the retinal characteristics of ROP (disease process). The combined contribution of these factors with immaturity at birth (as intrinsic risk modifier) and prenatal inflammation (as extrinsic facilitator) seems to provide a cogent functional framework of ROP occurrence. Finally, we apply the Bradford Hill heuristics to the available evidence. Taken together, the above suggests that neonatal sepsis is a causal inducer of ROP.
Keywords: Infection; Inflammation; Newborn; Prematurity; Retinopathy; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Alshaikh B, et al., 2013. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants with neonatal sepsis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Perinatology 33, 558–564. - PubMed
-
- Aralikatti AK, et al., 2010. Is ethnicity a risk factor for severe retinopathy of prematurity? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 95, F174–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

