Angiotensin II in liver transplantation (AngLT-1): protocol of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 37984940
- PMCID: PMC10660907
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-078713
Angiotensin II in liver transplantation (AngLT-1): protocol of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Catecholamine vasopressors such as norepinephrine are the standard drugs used to maintain mean arterial pressure during liver transplantation. At high doses, catecholamines may impair organ perfusion. Angiotensin II is a peptide vasoconstrictor that may improve renal perfusion pressure and glomerular filtration rate, a haemodynamic profile that could reduce acute kidney injury. Angiotensin II is approved for vasodilatory shock but has not been rigorously evaluated for treatment of hypotension during liver transplantation. The objective is to assess the efficacy of angiotensin II as a second-line vasopressor infusion during liver transplantation. This trial will establish the efficacy of angiotensin II in decreasing the dose of norepinephrine to maintain adequate blood pressure. Completion of this study will allow design of a follow-up, multicentre trial powered to detect a reduction of organ injury in liver transplantation.
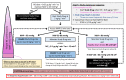
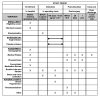
Methods and analysis: This is a double-blind, randomised clinical trial. Eligible subjects are adults with a Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Sodium Score ≥25 undergoing deceased donor liver transplantation. Subjects are randomised 1:1 to receive angiotensin II or saline placebo as the second-line vasopressor infusion. The study drug infusion is initiated on reaching a norepinephrine dose of 0.05 µg kg-1 min-1 and titrated per protocol. The primary outcome is the dose of norepinephrine required to maintain a mean arterial pressure ≥65 mm Hg. Secondary outcomes include vasopressin or epinephrine requirement and duration of hypotension. Safety outcomes include incidence of thromboembolism within 48 hours of the end of surgery and severe hypertension. An intention-to-treat analysis will be performed for all randomised subjects receiving the study drug. The total dose of norepinephrine will be compared between the two arms by a one-tailed Mann-Whitney U test.
Ethics and dissemination: The trial protocol was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (#20-30948). Results will be posted on ClinicalTrials.gov and published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.govNCT04901169.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Blood Pressure; End Stage Liver Disease; Liver Cirrhosis; Liver Transplantation; Vasoconstrictor agents.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MB discloses that support was provided by La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company (now Innoviva, Waltham, MA, USA) for this trial as part of an investigator-initiated research proposal. This support consisted of study drug (AngII) at no cost for trial patients only, and $14 231 USD (direct plus indirect costs) to support an assistant research coordinator. La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company reviewed the protocol before trial initiation but suggested no changes. The authors have sole responsibility (independent of La Jolla Pharmaceutical/Innoviva) for conduct of the trial, analysis and interpretation of data, assignment of adverse events and dissemination of results. ML has received consulting fees from La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company, Alexion Pharmaceuticals and SphingoTec GmbH. All other authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock 3 (ATHOS-3): protocol for a phase III, double-blind, randomised controlled trial.Crit Care Resusc. 2017 Mar;19(1):43-49. Crit Care Resusc. 2017. PMID: 28215131 Clinical Trial.
-
A Prospective double-blind, randomised controlled trial comparing angiotensin II to norepinephrine to reduce length of hospital stay in cardiac surgery patients (the PORTHOS study protocol).BMJ Open. 2025 Apr 15;15(4):e095099. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-095099. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40233952 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II and Vasopressin for Vasodilatory Shock: A Critical Appraisal of Catecholamine-Sparing Strategies.J Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun;36(6):635-645. doi: 10.1177/0885066620911601. Epub 2020 Mar 30. J Intensive Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32223515 Review.
-
Novel Vasopressors in the Treatment of Vasodilatory Shock: A Systematic Review of Angiotensin II, Selepressin, and Terlipressin.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 Apr;35(4):327-337. doi: 10.1177/0885066618818460. Epub 2018 Dec 18. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 30563433
Cited by
-
New drugs for acute kidney injury.J Intensive Med. 2024 Sep 7;5(1):3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2024.08.001. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Intensive Med. 2024. PMID: 39872831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II as a Vasopressor for Perioperative Hypotension in Solid Organ Transplant.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 9;12(8):1817. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081817. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A retrospective cohort analysis comparing the effectiveness and safety of perioperative angiotensin II to adrenergic vasopressors as a first-line vasopressor in kidney transplant recipients.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 Oct 17;4(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00207-w. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 39420433 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressin Is Not Associated With Severe Kidney Injury in Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-adjusted Analysis.Transplant Direct. 2025 May 21;11(6):e1814. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001814. eCollection 2025 Jun. Transplant Direct. 2025. PMID: 40406183 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
