Association of antecedent statin use on 30-day, 60-day and 90-day mortality among Mississippi Medicaid beneficiaries diagnosed with COVID-19
- PMID: 37984946
- PMCID: PMC10660820
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076195
Association of antecedent statin use on 30-day, 60-day and 90-day mortality among Mississippi Medicaid beneficiaries diagnosed with COVID-19
Abstract
Objective: To assess if the antecedent statin use was associated with all-cause death among COVID-19 patients enrolled in Medicaid.
Design: Cohort study.
Setting: Mississippi Medicaid population.
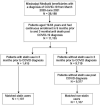
Participants: This study included 10 792 Mississippi Medicaid-enrolled patients between 18 and 64 years of age with a confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis from March 2020 to June 2021.
Intervention: Antecedent statin use, which was determined by a record of statin prescription in the 90-day period prior to the COVID diagnosis.
Main outcome measures: The outcomes of interest included mortality from all cause within 30 days, 60 days and 90 days after index.
Results: A total of 10 792 patients with COVID-19 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria, with 13.1% of them being antecedent statin users. Statin users were matched 1:1 with non-users based on age, sex, race, comorbidities and medication use by propensity score matching. In total, the matched cohort consisted of 1107 beneficiaries in each group. Multivariable logistic regression showed that statin users were less likely to die within 30 days (adjusted OR: 0.51, 95% CI: 0.32 to 0.83), 60 days (OR: 0.56, 95% CI: 0.37 to 0.85) and 90 days (OR: 0.55, 95% CI: 0.37 to 0.82) after diagnosis of COVID-19. Those with low-intensity/moderate-intensity statin use had significantly lower mortality risk in the 60-day and the 90-day follow-up period, while the high intensity of statin use was only found to be significantly associated with a lower odd of mortality within 30 days post index.
Conclusion: After COVID infection, Medicaid beneficiaries who had taken statins antecedently could be at lower risk for death. For patients with chronic conditions, continuity of care is crucial when interruptions occur in their medical care. Further research is required to further investigate the potential mechanisms and optimal use of statins in COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; chronic disease; lipid disorders; mortality; retrospective studies.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: TK and DS are Mississippi Division of Medicaid employees. The work reported was conducted by the MS-DUR program in the Center for Pharmaceutical Marketing and Management as part of the retrospective drug use analysis activities conducted under contract with the Mississippi Division of Medicaid. The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Mississippi Division of Medicaid or the University of Mississippi.
Figures
References
-
- CDC . Cases, data, and surveillance. centers for disease control and prevention. 2020. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/cases-updates/burden.html
-
- CDC . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). centers for disease control and prevention. 2020. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/data-review/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous