Protocol for SNOTOB study: radical prostatectomy without prostate biopsy following 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT based on a diagnostic model: a single-centre, single-arm, open-label study
- PMID: 37984956
- PMCID: PMC10660686
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-073983
Protocol for SNOTOB study: radical prostatectomy without prostate biopsy following 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT based on a diagnostic model: a single-centre, single-arm, open-label study
Abstract
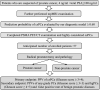
Introduction: Nowadays, invasive prostate biopsy is the standard diagnostic test for patients with suspected prostate cancer (PCa). However, it has some shortcomings such as perioperative complications, economic and psychological burden on patients, and some patients may undergo repeated prostate biopsy. In this study protocol, our aim is to provide a non-invasive diagnostic strategy we call the 'prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) combined model' for the diagnosis of PCa. If patients are diagnosed with PCa using PSMA combined model, we want to prove these patients can receive radical prostatectomy directly without prior prostate biopsies.
Methods: The SNOTOB trial adopts a prospective, single-centre, single-arm, open-label study design. The PSMA combined model consists of a diagnostic model based on what we previously reported and 18F-PSMA-1007 positron emission tomography/CT (18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT) examinations in series. First, patients use the diagnostic model (online address: https://ustcprostatecancerprediction.shinyapps.io/dynnomapp/) to calculate the risk probability of clinically significant PCa (csPCa). When the risk probability of csPCa is equal or greater than 0.60, 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT will be applied for further diagnosis. If patients are still considered as csPCa after 18F-PSMA-1007 PET/CT examinations, we define this condition as positive results of PSMA combined model. Subsequently, we will recommend these patients to accept radical prostatectomy without prostate biopsy directly. Finally, the diagnostic performance of PSMA combined model will be verified with the pathological results. Totally, 57 patients need to be enrolled in this clinical trial.
Ethics and dissemination: This study was approved by the ethics committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC (No. 2022KY-142). The results of this study will be published in peer-reviewed journals and reported at academic conferences.
Trial registration number: NCT05587192.
Keywords: biopsy; diagnostic radiology; prostatic neoplasms; protocols & guidelines.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protocol for the PRIMARY clinical trial, a prospective, multicentre, cross-sectional study of the additive diagnostic value of gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen positron-emission tomography/computed tomography to multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnostic setting for men being investigated for prostate cancer.BJU Int. 2020 Apr;125(4):515-524. doi: 10.1111/bju.14999. Epub 2020 Feb 12. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 31957122
-
18F-fluciclovine PET-CT and 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET-CT in patients with early biochemical recurrence after prostatectomy: a prospective, single-centre, single-arm, comparative imaging trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Sep;20(9):1286-1294. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30415-2. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31375469 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Detection of prostate cancer with 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT compared to final histopathology of radical prostatectomy specimens: is PSMA-targeted biopsy feasible? The DeTeCT trial.World J Urol. 2021 Jul;39(7):2439-2446. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03490-8. Epub 2020 Oct 20. World J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33079250 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
68Ga-Labeled Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Ligand Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur Urol Focus. 2018 Sep;4(5):686-693. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Eur Urol Focus. 2018. PMID: 28753806
-
Use of gallium-68 prostate-specific membrane antigen positron-emission tomography for detecting lymph node metastases in primary and recurrent prostate cancer and location of recurrence after radical prostatectomy: an overview of the current literature.BJU Int. 2020 Feb;125(2):206-214. doi: 10.1111/bju.14944. Epub 2019 Nov 29. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 31680398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of LncRNA PSMA3-AS1 in prostate cancer and its potential regulatory mechanism.Hereditas. 2025 Jul 12;162(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00485-6. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40652273 Free PMC article.
-
Radical prostatectomy without prostate biopsy based on a noninvasive diagnostic strategy: a prospective single-center study.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025 Jun;28(2):496-502. doi: 10.1038/s41391-024-00931-y. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. PMID: 39695194
-
Comparative efficacy of radical prostatectomy and radiotherapy in the treatment of high-risk prostate cancer.Technol Health Care. 2024;32(6):4671-4679. doi: 10.3233/THC-240910. Technol Health Care. 2024. PMID: 39093097 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
