[Drug Resistance Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategy of Targeted Therapy of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with MET Alterations]
- PMID: 37985154
- PMCID: PMC10600752
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.102.33
[Drug Resistance Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategy of Targeted Therapy of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with MET Alterations]
Abstract
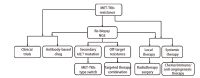
Mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor (MET) gene alterations involve in the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. MET-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been approved to treat non-small cell lung cancer with MET alterations, and resistance to these TKIs is inevitable. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to MET-TKIs are completely unclear. The review focused on potential mechanisms of MET-TKIs resistance and therapeutics strategies to delay and prevent resistance. .
【中文题目:MET基因改变的非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗 耐药机制及治疗策略】 【中文摘要:间质表皮转化因子(mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor, MET)基因改变参与了非小细胞肺癌的增殖、侵袭和转移。MET-酪氨酸激酶抑制剂(tyrosine kinase inhibitors, TKIs)已获批用于MET基因改变的非小细胞肺癌,而这些药物的耐药不可避免。MET-TKIs的分子耐药机制错综复杂,尚不完全清楚。本文主要对这些MET-TKIs的潜在耐药机制进行综述,以期为MET基因改变的患者提供合理的治疗思路。 】 【中文关键词:肺肿瘤;间质表皮转化因子;靶向治疗;耐药;治疗策略】.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Lung neoplasms; Mesenchymal to epithelial transition factor; Targeted therapy; Treatment strategy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined inhibition of MEK and PI3K pathways overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2018 Oct;109(10):3183-3196. doi: 10.1111/cas.13763. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 30098066 Free PMC article.
-
[Research Progress of Acquired Resistance Mediated by MET Amplification in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Aug 20;25(8):615-621. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.102.23. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36002199 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Dec;12(Supplement):C131-C137. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.200613. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 28230005 Review.
-
Contribution of p53 in sensitivity to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 4;11(1):19667. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99267-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34608255 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44332-45. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6293. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26554308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous