Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs
- PMID: 37985700
- PMCID: PMC10954414
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-023-01548-3
Combinatorial development of nebulized mRNA delivery formulations for the lungs
Abstract
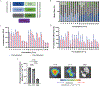
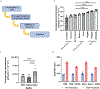
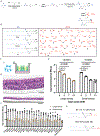
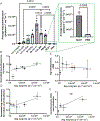
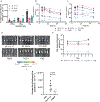
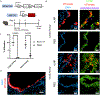
Inhaled delivery of mRNA has the potential to treat a wide variety of diseases. However, nebulized mRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) face several unique challenges including stability during nebulization and penetration through both cellular and extracellular barriers. Here we develop a combinatorial approach addressing these barriers. First, we observe that LNP formulations can be stabilized to resist nebulization-induced aggregation by altering the nebulization buffer to increase the LNP charge during nebulization, and by the addition of a branched polymeric excipient. Next, we synthesize a combinatorial library of ionizable, degradable lipids using reductive amination, and evaluate their delivery potential using fully differentiated air-liquid interface cultured primary lung epithelial cells. The final combination of ionizable lipid, charge-stabilized formulation and stability-enhancing excipient yields a significant improvement in lung mRNA delivery over current state-of-the-art LNPs and polymeric nanoparticles.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.Y.J., J.W., I.O.R. and D.G.A. have filed a patent for the biodegradable lipid library described herein (US Patent Application No. 18080299). D.G.A. receives research funding from Sanofi/Translate Bio, and is a founder of oRNA Tx. R.L. is co-founder and a director of Moderna. He also serves on the board and has equity in Particles For Humanity. For a list of entities with which R.L. is, or has been recently involved, compensated or uncompensated, see
Figures
References
-
- Hajj KA & Whitehead KA Tools for translation: non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater 2, 1–17 (2017).
-
- Swingle KL, Hamilton AG & Mitchell MJ Lipid nanoparticle-mediated delivery of mRNA therapeutics and vaccines. Trends Mol. Med 27, 616–617 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

