Clinical impact using low-dose mycophenolate mofetil with tacrolimus on infectious, noninfectious complications and acute rejection, in renal transplant: A single hospital experience in Mexico
- PMID: 37986377
- PMCID: PMC10659689
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035841
Clinical impact using low-dose mycophenolate mofetil with tacrolimus on infectious, noninfectious complications and acute rejection, in renal transplant: A single hospital experience in Mexico
Abstract
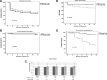
Evidence supporting a starting dose of 2 g/day of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in combination with tacrolimus (TAC) for renal transplantation (RT) is still limited, but maintaining a dose of <2 g could result in worse clinical outcomes in terms of acute rejection (AR). This study aimed to determine the association between AR and infectious and noninfectious complications after RT with a dose of 1.5 g vs 2 g of MMF. A prospective cohort study was performed with a 12-month follow-up of recipients of RT from living donors with low (1.5 g/day) or standard (2 g/day) doses of MMF. The association between adverse effects and complications and doses of MMF was examined using Cox proportional hazard models, and survival free of AR, infectious diseases, and noninfectious complications was evaluated using the Kaplan-Meier test. At the end of the follow-up, the incidence of infectious diseases was 52% versus 50% (P = .71) and AR was 5% versus 5% (P = .86), respectively. The survival rate free of gastrointestinal (GI) complications requiring medical attention was higher in the low-dose group than in the standard-dose dose (88% vs 45%, respectively; P < .001). The use of 1.5 g/day of MMF confers a reduction in GI complications without an increase in infectious diseases or the risk of AR.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of tacrolimus in combination with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in cadaveric renal transplant recipients. FK506/MMF Dose-Ranging Kidney Transplant Study Group.Transplantation. 2000 Mar 15;69(5):875-80. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200003150-00035. Transplantation. 2000. PMID: 10755543 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose optimization of mycophenolate mofetil when administered with a low dose of tacrolimus in cadaveric renal transplant recipients.Transplantation. 2001 Jul 15;72(1):63-9. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200107150-00014. Transplantation. 2001. PMID: 11468536 Clinical Trial.
-
A Prospective Randomized, Comparative Trial of High-Dose Mizoribine Versus Mycophenolate Mofetil in Combination With Tacrolimus and Basiliximab for Living Donor Renal Transplant: A Multicenter Trial.Exp Clin Transplant. 2016 Oct;14(5):518-525. Exp Clin Transplant. 2016. PMID: 27733107 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term kidney allograft function and survival in prednisone-free regimens: tacrolimus/mycophenolate mofetil versus tacrolimus/sirolimus.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Mar;7(3):504-12. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06940711. Epub 2012 Jan 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22282478 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tacrolimus plus low-dose mycophenolate mofetil in renal transplant recipients: better 2-year graft and patient survival than with a higher mycophenolate mofetil dose.Transplant Proc. 2005 Sep;37(7):3009-11. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.07.033. Transplant Proc. 2005. PMID: 16213288 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Andrade Sierra J, Hernández Reyes H, Rojas C, et al. . Clinical impact using low dose mycophenolate mofetil with tacrolimus on acute rejection, infectious diseases and non-infectious complications in renal transplant: A Single Hospital Experience in Mexico. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.29.22282803v1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gamal M, Salah AM, Hendy YA, et al. . Death with a functioning graft kidney: a single-center experience of more than 4 decades. Exp Clin Transplant. 2022;20:136–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials