This is a preprint.
Development of a Liver Disease-Specific Large Language Model Chat Interface using Retrieval Augmented Generation
- PMID: 37986764
- PMCID: PMC10659484
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.10.23298364
Development of a Liver Disease-Specific Large Language Model Chat Interface using Retrieval Augmented Generation
Update in
-
Development of a liver disease-specific large language model chat interface using retrieval-augmented generation.Hepatology. 2024 Nov 1;80(5):1158-1168. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000834. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Hepatology. 2024. PMID: 38451962 Free PMC article.
Abstract
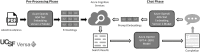
Background: Large language models (LLMs) have significant capabilities in clinical information processing tasks. Commercially available LLMs, however, are not optimized for clinical uses and are prone to generating incorrect or hallucinatory information. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is an enterprise architecture that allows embedding of customized data into LLMs. This approach "specializes" the LLMs and is thought to reduce hallucinations.
Methods: We developed "LiVersa," a liver disease-specific LLM, by using our institution's protected health information (PHI)-complaint text embedding and LLM platform, "Versa." We conducted RAG on 30 publicly available American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) guidelines and guidance documents to be incorporated into LiVersa. We evaluated LiVersa's performance by comparing its responses versus those of trainees from a previously published knowledge assessment study regarding hepatitis B (HBV) treatment and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance.
Results: LiVersa answered all 10 questions correctly when forced to provide a "yes" or "no" answer. Full detailed responses with justifications and rationales, however, were not completely correct for three of the questions.
Discussions: In this study, we demonstrated the ability to build disease-specific and PHI-compliant LLMs using RAG. While our LLM, LiVersa, demonstrated more specificity in answering questions related to clinical hepatology - there were some knowledge deficiencies due to limitations set by the number and types of documents used for RAG. The LiVersa prototype, however, is a proof of concept for utilizing RAG to customize LLMs for clinical uses and a potential strategy to realize personalized medicine in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors of this manuscript have the following potential conflicts of interest to disclose: - Dr. Jin Ge receives research support from Merck and Co; and consults for Astellas Pharmaceuticals/Iota Biosciences. - Dr. Jennifer C. Lai receives research support from Lipocene and Vir Biotechnologies; receives an education grant from Nestle Nutrition Sciences; serves on an advisory board for Novo Nordisk; and consults for Genfit, Third Rock Ventures, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- Rahman M, Terano HJR, Rahman N, Salamzadeh A, Rahaman S. Chatgpt and academic research: A review and recommendations based on practical examples. J Educ, Mngt, and Dev Studies. 2023;3(1):1–12.
-
- ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue. Accessed December 17, 2022. https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt/
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources