This is a preprint.
Dynamic RNA Polymerase II Recruitment Drives Differentiation of the Intestine under the direction of HNF4
- PMID: 37986803
- PMCID: PMC10659318
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.08.566322
Dynamic RNA Polymerase II Recruitment Drives Differentiation of the Intestine under the direction of HNF4
Update in
-
Dynamic RNA polymerase II occupancy drives differentiation of the intestine under the direction of HNF4.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114242. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114242. Epub 2024 May 19. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38768033 Free PMC article.
Abstract
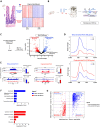
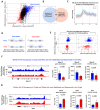
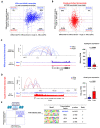
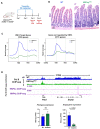
Terminal differentiation requires a massive restructuring of the transcriptome. During intestinal differentiation, the expression patterns of nearly 4000 genes are altered as cells transition from progenitor cells in crypts to differentiated cells in villi. We identified dynamic recruitment of RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) to gene promoters as the primary driver of transcriptomic shifts during intestinal differentiation in vivo. Changes in enhancer-promoter looping interactions accompany dynamic Pol II recruitment and are dependent upon HNF4, a pro-differentiation transcription factor. Using genetic loss-of- function, ChIP-seq and IP mass spectrometry, we demonstrate that HNF4 collaborates with chromatin remodelers and loop-stabilizing proteins and facilitates Pol II recruitment at hundreds of genes pivotal to differentiation. We also explore alternate mechanisms which drive differentiation gene expression and find pause-release of Pol II and post- transcriptional mRNA stability regulate smaller subsets of differentially expressed genes. These studies provide insights into the mechanisms of differentiation in a renewing adult tissue.
Keywords: HNF4 transcription factors; Pol II ChIP; RNA polymerase II; chromatin looping; crypt-villus axis; dynamic Pol II recruitment; intestinal epithelium; post-transcriptional regulation; promoter-proximal pausing; rapid immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry of endogenous proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
