This is a preprint.
A vasopressin circuit that modulates sex-specific social interest and anxiety-like behavior in mice
- PMID: 37986987
- PMCID: PMC10659331
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.06.564847
A vasopressin circuit that modulates sex-specific social interest and anxiety-like behavior in mice
Update in
-
A vasopressin circuit that modulates mouse social investigation and anxiety-like behavior in a sex-specific manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 14;121(20):e2319641121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2319641121. Epub 2024 May 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38709918 Free PMC article.
Abstract
One of the largest sex differences in brain neurochemistry is the male-biased expression of the neuropeptide arginine vasopressin (AVP) within the vertebrate social brain. Despite the long-standing implication of AVP in social and anxiety-like behavior, the precise circuitry and anatomical substrate underlying its control are still poorly understood. By employing optogenetic manipulation of AVP cells within the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), we have unveiled a central role for these cells in promoting social investigation, with a more pronounced role in males relative to females. These cells facilitate male social investigation and anxiety-like behavior through their projections to the lateral septum (LS), an area with the highest density of sexually-dimorphic AVP fibers. Blocking the vasopressin 1a receptor (V1aR) in the LS eliminated stimulation-mediated increases in these behaviors. Together, these findings establish a distinct BNST AVP → LS V1aR circuit that modulates sex-specific social interest and anxiety-like behavior.
Figures
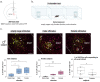


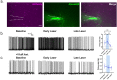


References
-
- Aspesi D., Choleris E., Neuroendocrine underpinning of social recognition in males and females. J. Neuroendocrinol. 34, e13070 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
