Gait Variability at Different Walking Speeds
- PMID: 37987494
- PMCID: PMC10660777
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk8040158
Gait Variability at Different Walking Speeds
Abstract
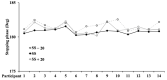
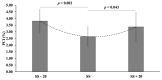
Gait variability (GV) is a crucial measure of inconsistency of muscular activities or body segmental movements during repeated tasks. Hence, GV might serve as a relevant and sensitive measure to quantify adjustments of walking control. However, it has not been clarified whether GV is associated with walking speed, a clarification needed to exploit effective better bilateral coordination level. For this aim, fourteen male students (age 22.4 ± 2.7 years, body mass 74.9 ± 6.8 kg, and body height 1.78 ± 0.05 m) took part in this study. After three days of walking 1 km each day at a self-selected speed (SS) on asphalt with an Apple Watch S. 7 (AppleTM, Cupertino, CA, USA), the participants were randomly evaluated on a treadmill at three different walking speed intensities for 10 min at each one, SS - 20%/SS + 20%/ SS, with 5 min of passive recovery in-between. Heart rate (HR) was monitored and normalized as %HRmax, while the rate of perceived exertion (RPE) (CR-10 scale) was asked after each trial. Kinematic analysis was performed, assessing the Contact Time (CT), Swing Time (ST), Stride Length (SL), Stride Cycle (SC), and Gait Variability as Phase Coordination Index (PCI). RPE and HR increased as the walking speed increased (p = 0.005 and p = 0.035, respectively). CT and SC decreased as the speed increased (p = 0.0001 and p = 0.013, respectively), while ST remained unchanged (p = 0.277). SL increased with higher walking speed (p = 0.0001). Conversely, PCI was 3.81 ± 0.88% (high variability) at 3.96 ± 0.47 km·h-1, 2.64 ± 0.75% (low variability) at SS (4.94 ± 0.58 km·h-1), and 3.36 ± 1.09% (high variability) at 5.94 ± 0.70 km·h-1 (p = 0.001). These results indicate that while the metabolic demand and kinematics variables change linearly with increasing speed, the most effective GV was observed at SS. Therefore, SS could be a new methodological approach to choose the individual walking speed, normalize the speed intensity, and avoid a gait pattern alteration.
Keywords: gait analysis; human locomotion; kinematic analysis; physiological response; symmetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous