Molecular Organization of the Skin Barrier
- PMID: 37987626
- PMCID: PMC10680981
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v103.13356
Molecular Organization of the Skin Barrier
Abstract
Cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections allows for investigation directly in situ of the molecular architecture of skin. Recently, this technique has contributed to the elucidation of the molecular organization of the skin's permeability barrier and its stepwise formation process. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the procedure for cryo-electron microscopy of vitreous sections, its analysis using atomic detail molecular dynamics modelling and electron microscopy simulation, and its application in the investigation of the barrier structure and formation process of the skin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
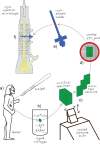
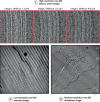


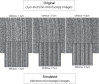




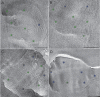
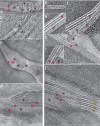


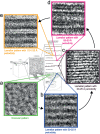
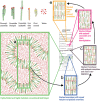

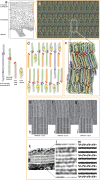
References
-
- Duriau F. Recherches expérimentales sur l’absorption et l’exhalation par le té́gument externe. Arch Gen Med T 1856; 7: 161–173.
-
- Homolle A. Expériences physiologiques sur l’absorption par la tégument externe chez l’homme dans le bain. Union Med 1853; 7: 462.
-
- Winsor TB, Burch GE. Differential roles of layers of human epigastric skin on diffusion rate of water. Arch Intern Med 1944; 74: 428–436.
-
- Berenson GS, Burch GE. Studies of diffusion of water through dead human skin; the effect of different environmental states and of chemical alterations of the epidermis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1951; 31: 842–853. - PubMed
-
- Blank IH. Factors which influence the water content of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol 1952; 18: 433–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

