Two Synthetic Tools to Deepen the Understanding of the Influence of Stereochemistry on the Properties of Iridium(III) Heteroleptic Emitters
- PMID: 37988596
- PMCID: PMC10880056
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c03133
Two Synthetic Tools to Deepen the Understanding of the Influence of Stereochemistry on the Properties of Iridium(III) Heteroleptic Emitters
Abstract
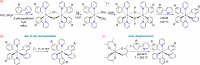
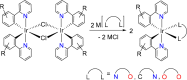
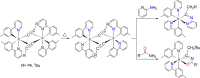
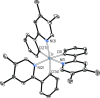
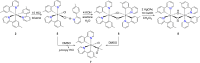
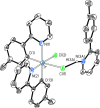
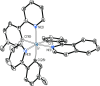
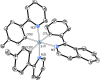
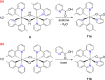
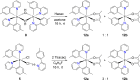
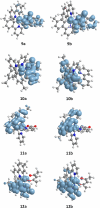
Two complementary procedures are presented to prepare cis-pyridyl-iridium(III) emitters of the class [3b+3b+3b'] with two orthometalated ligands of the 2-phenylpyridine type (3b) and a third ligand (3b'). They allowed to obtain four emitters of this class and to compare their properties with those of the trans-pyridyl isomers. The finding starts from IrH5(PiPr3)2, which reacts with 2-(p-tolyl)pyridine to give fac-[Ir{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}3] with an almost quantitative yield. Stirring the latter in the appropriate amount of a saturated solution of HCl in toluene results in the cis-pyridyl adduct IrCl{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ1-Cl-[Cl-H-py-C6MeH4]} stabilized with p-tolylpyridinium chloride, which can also be transformed into dimer cis-[Ir(μ-OH){κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2]2. Adduct IrCl{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ1-Cl-[Cl-H-py-C6MeH4]} directly generates cis-[Ir{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ2-C,N-[C6H4-Isoqui]}] and cis-[Ir{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ2-C,N-[C6H4-py]}] by transmetalation from Li[2-(isoquinolin-1-yl)-C6H4] and Li[py-2-C6H4]. Dimer cis-[Ir(μ-OH){κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2]2 is also a useful starting complex when the precursor molecule of 3b' has a fairly acidic hydrogen atom, suitable for removal by hydroxide groups. Thus, its reactions with 2-picolinic acid and acetylacetone (Hacac) lead to cis-Ir{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ2-O,N-[OC(O)-py]} and cis-Ir{κ2-C,N-[C6MeH3-py]}2{κ2-O,O-[acac]}. The stereochemistry of the emitter does not significantly influence the emission wavelengths. On the contrary, its efficiency is highly dependent on and associated with the stability of the isomer. The more stable isomer shows a higher quantum yield and color purity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Baldo M. A.; O’Brien D. F.; You Y.; Shoustikov A.; Sibley S.; Thompson M. E.; Forrest S. R. Highly efficient phosphorescent emission from organic electroluminescent devices. Nature 1998, 395, 151–154. 10.1038/25954. - DOI
-
- Chou P.-T.; Chi Y.; Chung M.-W.; Lin C.-C. Harvesting luminescence via harnessing the photophysical properties of transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2653–2665. 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.12.013. - DOI
- Powell B. J. Theories of phosphorescence in organo-transition metal complexes – From relativistic effects to simple models and design principles for organic light-emitting diodes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 295, 46–79. 10.1016/j.ccr.2015.02.008. - DOI
-
- Yersin H.; Rausch A. F.; Czerwieniec R.; Hofbeck T.; Fischer T. The triplet state of organo-transition metal compounds. Triplet harvesting and singlet harvesting for efficient OLEDs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2622–2652. 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.042. - DOI
-
- Baranoff E.; Yum J.-H.; Graetzel M.; Nazeeruddin M. D. Cyclometallated iridium complexes for conversion of light into electricity and electricity into light. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2661–2670. 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2009.02.033. - DOI
- Xiao L.; Chen Z.; Qu B.; Luo J.; Kong S.; Gong Q.; Kido J. Recent Progresses on Materials for Electrophosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Devices. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 926–952. 10.1002/adma.201003128. - DOI - PubMed
- Fan C.; Yang C. Yellow/orange emissive heavy-metal complexes as phosphors in monochromatic and white organic light-emitting devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6439–6469. 10.1039/C4CS00110A. - DOI - PubMed
- Yang X.; Zhou G.; Wong W.-Y. Functionalization of phosphorescent emitters and their host materials by main-group elements forphosphorescent organic light-emitting devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8484–8575. 10.1039/C5CS00424A. - DOI - PubMed
- Jou J.-H.; Kumar K.; Agrawal A.; Li T.-H.; Sahoo S. Approaches for fabricating high efficiency organic light emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2974–3002. 10.1039/C4TC02495H. - DOI
- Huo S.; Carroll J.; Vezzu D. A. K. Design, Synthesis, and Applications of Highly Phosphorescent Cyclometalated Platinum Complexes. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2015, 4, 1210–1245. 10.1002/ajoc.201500246. - DOI
- Lu C.-W.; Wang Y.; Chi Y. Metal Complexes with Azolate-Functionalized Multidentate Ligands: Tactical Designs and Optoelectronic Applications. Chem.—Eur. J. 2016, 22, 17892–17908. 10.1002/chem.201601216. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atwood J. D.Inorganic and Organometallic Reaction Mechanisms; VCH: New York, 1997; Chapter 3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

