Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
- PMID: 37989734
- PMCID: PMC10663519
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42637-0
Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
Abstract
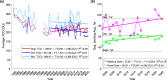
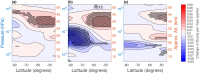
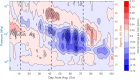
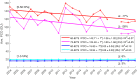
The past three years (2020-2022) have witnessed the re-emergence of large, long-lived ozone holes over Antarctica. Understanding ozone variability remains of high importance due to the major role Antarctic stratospheric ozone plays in climate variability across the Southern Hemisphere. Climate change has already incited new sources of ozone depletion, and the atmospheric abundance of several chlorofluorocarbons has recently been on the rise. In this work, we take a comprehensive look at the monthly and daily ozone changes at different altitudes and latitudes within the Antarctic ozone hole. Following indications of early-spring recovery, the October middle stratosphere is dominated by continued, significant ozone reduction since 2004, amounting to 26% loss in the core of the ozone hole. We link the declines in mid-spring Antarctic ozone to dynamical changes in mesospheric descent within the polar vortex, highlighting the importance of continued monitoring of the state of the ozone layer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Meteorological Organization. Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2022. GAW Report 278, (WMO, Geneva, 2022).
-
- Anderson J, Russell III JM, Solomon S, Deaver LE. Halogen Occultation Experiment confirmation of stratospheric chlorine decreases in accordance with the Montreal Protocol. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmosph. 2000;105:4483–4490. doi: 10.1029/1999JD901075. - DOI
-
- Solomon, P. et al. Rise and decline of active chlorine in the stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett.33 (18) 10.1029/2006GL027029 (2006).
-
- Chubachi, S. A Special Ozone Observation at Syowa Station, Antarctica from February 1982 to January 1983. In: Zerefos, C.S., Ghazi, A. (eds.) Atmospheric Ozone, pp. 285–289. Springer, Dordrecht 10.1007/978-94-009-5313-0_58 (1985).
-
- Farman JC, Gardiner BG, Shanklin JD. Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction. Nature. 1985;315:207–210. doi: 10.1038/315207a0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

