Quantification of ligand and mutation-induced bias in EGFR phosphorylation in direct response to ligand binding
- PMID: 37989743
- PMCID: PMC10663608
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42926-8
Quantification of ligand and mutation-induced bias in EGFR phosphorylation in direct response to ligand binding
Abstract
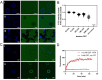
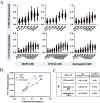
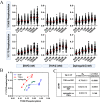
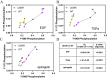
Signaling bias is the ability of a receptor to differentially activate downstream signaling pathways in response to different ligands. Bias investigations have been hindered by inconsistent results in different cellular contexts. Here we introduce a methodology to identify and quantify bias in signal transduction across the plasma membrane without contributions from feedback loops and system bias. We apply the methodology to quantify phosphorylation efficiencies and determine absolute bias coefficients. We show that the signaling of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) to EGF and TGFα is biased towards Y1068 and against Y1173 phosphorylation, but has no bias for epiregulin. We further show that the L834R mutation found in non-small-cell lung cancer induces signaling bias as it switches the preferences to Y1173 phosphorylation. The knowledge gained here challenges the current understanding of EGFR signaling in health and disease and opens avenues for the exploration of biased inhibitors as anti-cancer therapies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

