Targeting IL-6 or IL-6 Receptor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Have We Learned?
- PMID: 37989892
- PMCID: PMC10789669
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-023-00634-1
Targeting IL-6 or IL-6 Receptor in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Have We Learned?
Abstract
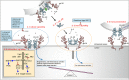
The use of different pathways in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis has led to a significant decrease in the number of treatment-resistant patients. In this context, interleukin (IL)-6 inhibition has filled an important gap in rheumatoid arthritis treatment with its effectiveness and safety in both monotherapy and combinations. The process of IL-6 inhibition initiated with IL-6 receptor blockers has prompted questions regarding the potential impact and safety of different inhibitions of this pathway, such as the direct blockade of IL-6. Following the termination of the development of sirukumab because of mortality data in early studies, the investigation of olokizumab, which targets a different region of the IL-6 cytokine, has renewed the hope in this area and the safety concerns have been largely alleviated by the open-label extension data. In addition, the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab and sarilumab have led to a rapid investigation of biosimilars and new potent IL-6 receptor blockers. A comprehensive understanding of mechanisms of this pathway with further long-term clinical data and basic research may provide a decisive impact on selecting the appropriate mechanism as the first choice in personalized treatments.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ali Berkant Avci has no conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this article. Eugen Feist has received honoraria for lectures as an advisor from AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Galapagos, Lilly, Medac, Novartis, Pfizer, Sobi, and Sanofi. Gerd R. Burmester has received honoraria for consulting and lectures from Chugai and Sanofi.
Figures

References
-
- Kraakman MJ, Kammoun HL, Allen TL, Deswaerte V, Henstridge DC, Estevez E, et al. Blocking IL-6 trans-signaling prevents high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue macrophage recruitment but does not improve insulin resistance. Cell Metabol. 2015;21(3):403–416. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.02.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

