Structure and function of the membrane microdomains in osteoclasts
- PMID: 37989999
- PMCID: PMC10663511
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-023-00294-5
Structure and function of the membrane microdomains in osteoclasts
Abstract
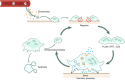
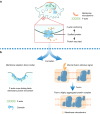
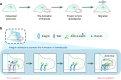
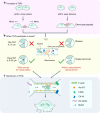
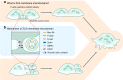
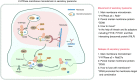
The cell membrane structure is closely related to the occurrence and progression of many metabolic bone diseases observed in the clinic and is an important target to the development of therapeutic strategies for these diseases. Strong experimental evidence supports the existence of membrane microdomains in osteoclasts (OCs). However, the potential membrane microdomains and the crucial mechanisms underlying their roles in OCs have not been fully characterized. Membrane microdomain components, such as scaffolding proteins and the actin cytoskeleton, as well as the roles of individual membrane proteins, need to be elucidated. In this review, we discuss the compositions and critical functions of membrane microdomains that determine the biological behavior of OCs through the three main stages of the OC life cycle.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Foreign body giant cells and osteoclasts are TRAP positive, have podosome-belts and both require OC-STAMP for cell fusion.J Cell Biochem. 2013 Aug;114(8):1772-8. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24518. J Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23444125
-
Linking membrane microdomains to the cytoskeleton: regulation of the lateral mobility of reggie-1/flotillin-2 by interaction with actin.FEBS Lett. 2007 Oct 2;581(24):4697-703. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.08.074. Epub 2007 Sep 6. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17854803
-
Membrane microdomains and proteomics: lessons from tetraspanin microdomains and comparison with lipid rafts.Proteomics. 2006 Dec;6(24):6447-54. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200600282. Proteomics. 2006. PMID: 17109380 Review.
-
Caveolin limits membrane microdomain mobility and integrin-mediated uptake of fibronectin-binding pathogens.J Cell Sci. 2010 Dec 15;123(Pt 24):4280-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.064006. Epub 2010 Nov 23. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 21098633
-
New Insight Into the Roles of Membrane Microdomains in Physiological Activities of Fungal Cells.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016;325:119-80. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2016.02.005. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27241220 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysosomal biogenesis and function in osteoclasts: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 7;12:1431566. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1431566. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39170917 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

