Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
- PMID: 37990070
- PMCID: PMC10663499
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-47682-9
Minimally invasive management of vital teeth requiring root canal therapy
Abstract
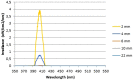
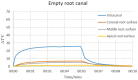
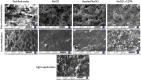
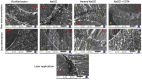
The present study aimed to investigate the possible use of a non-instrumentation technique including blue light irradiation for root canal cleaning. Extracted human single rooted teeth were selected. Nine different groups included distilled water, NaOCl, intra-canal heated NaOCl, and NaOCl + EDTA irrigation after either instrumentation or non-instrumentation, and a laser application group following non-instrumentation technique. The chemical assessment of the root canal dentine was evaluated using energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Surface microstructural analyses were performed by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The antimicrobial efficacy of different preparation techniques was evaluated using microbial tests. Light application didn't change the calcium/phosphorus, carbonate/phosphate and amide I/phosphate ratios of the root canal dentin. The root canal dentin preserved its original chemistry and microstructure after light application. The instrumentation decreased the carbonate/phosphate and amide I/phosphate ratios of the root canal dentin regardless of the irrigation solution or technique (p < 0.05). The application of light could not provide antibacterial efficacy to match the NaOCl irrigation. The NaOCl irrigation both in the non-instrumentation and instrumentation groups significantly reduced the number of bacteria (p < 0.05). The use of minimally invasive root canal preparation techniques where the root canal is not instrumented and is disinfected by light followed by obturation with a hydraulic cement sealer reduced the microbial load and preserved the dentin thus may be an attractive treatment option for management of vital teeth needing root canal therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Root Canal Dentin Erosion after Different Irrigation Methods Using Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy.J Endod. 2016 Dec;42(12):1834-1839. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.07.024. Epub 2016 Oct 18. J Endod. 2016. PMID: 27769680
-
Effect of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminotetraacetic acid activated by laser and ultrasonic energy on surface morphology and chemical composition of intracanal dentin.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Apr;87(4):818-831. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24474. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 38100184
-
Comparison of conventional, rotary, and ultrasonic preparation, different final irrigation regimens, and 2 sealers in primary molar root canal therapy.Pediatr Dent. 2006 Nov-Dec;28(6):518-23. Pediatr Dent. 2006. PMID: 17249433
-
The effect of initial irrigation with two different sodium hypochlorite concentrations on the erosion of instrumented radicular dentin.Dent Mater. 2010 Jun;26(6):514-23. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Dent Mater. 2010. PMID: 20181387 Clinical Trial.
-
Heated distilled water with or without continuous ultrasonic irrigation improves final irrigation efficacy and reduces dentine erosion.J Dent. 2020 Dec;103:103507. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103507. Epub 2020 Oct 21. J Dent. 2020. PMID: 33098929
Cited by
-
Assessment of a Light-Curable Hydrogel to Be Used for Root Canal Obturation.J Dent Res. 2025 Mar;104(3):260-269. doi: 10.1177/00220345241287504. Epub 2024 Dec 14. J Dent Res. 2025. PMID: 39673492 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Photodynamic Therapy With Two Different Photosensitizers on the Viability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells.J Lasers Med Sci. 2024 Dec 28;15:e70. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2024.70. eCollection 2024. J Lasers Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39949477 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of single-visit versus multiple-visit root canal therapy for chronic anterior apical periodontitis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):6804-6811. doi: 10.62347/OIPP9045. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39678596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haapasalo M, Endal U, Zandi H, Coil JM. Eradication of endodontic infection by instrumentation and irrigation solutions. Endod. Top. 2005;10:77–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-1546.2005.00135.x. - DOI
-
- Karataş E, Baltacı M, Uluköylü E, Adıgüzel A. Antibacterial effectiveness of calcium hydroxide alone or in combination with Ibuprofen and Ciprofloxacin in teeth with asymptomatic apical periodontitis: A randomized controlled clinical study. Int. Endod. J. 2020;53:742–753. doi: 10.1111/iej.13277. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Karataş E, Ayaz N, Uluköylü E, Baltaci MÖ, Adigüzel A. Effect of final irrigation with sodium hypochlorite at different temperatures on postoperative pain level and antibacterial activity: A randomized controlled clinical study. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2021;29:1–8. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2020-0502. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

