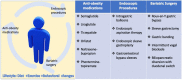
Obesity management for cardiovascular disease prevention
- PMID: 37990683
- PMCID: PMC10662048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.obpill.2023.100069
Obesity management for cardiovascular disease prevention
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a complex disease that leads to higher morbidity and mortality and its rate in the United States is rapidly rising. Targeting obesity management is one of the cornerstones of preventive medicine. Early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. While it is well known that lifestyle interventions such as healthful nutrition and routine physical activity are the first and most important step in management, some do not achieve the desired results and require further therapies.
Methods: A literature review was conducted, that included clinical documents, public scientific citations and peer review articles to evaluate anti-obesity medications, endoscopic procedures and bariatric surgeries in the management of obesity. We also included effects of these interventions on weight loss, cardiovascular disease risk reduction and side effects.
Results: This clinical review summarizes recent evidence for the different approaches in obesity management including medications, common endoscopic procedures and bariatric surgeries. For more detailed review on the different management options discussed, we recommend reviewing Obesity Medicine Association Clinical Practice Statement [1].
Conclusion: Management of obesity reduces cardiovascular risk, improves metabolic parameters and other important health outcomes. Different management approaches are available, hence, a high level of awareness of the growing epidemic of obesity is needed to ensure timely referrals to obesity medicine specialists.
Conflict of interest statement
We wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. We confirm that we have given due consideration to the protection of intellectual property associated with this work and that there are no impediments to publication, including the timing of publication, with respect to intellectual property. In so doing we confirm that we have followed the regulations of our institutions concerning intellectual property. We understand that the Corresponding Author is the sole contact for the Editorial process (including Editorial Manager and direct communications with the office). He/she is responsible for communicating with the other authors about progress, submissions of revisions and final approval of proofs. We confirm that we have provided a current, correct email address which is accessible by the Corresponding Author. Signed by all authors as follows.
Figures
References
-
- Hales C.M., Carroll M.D., Fryar C.D., Ogden C.L. vol. 360. NCHS Data Brief; 2020. (Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity among adults: United States, 2017–2018). - PubMed
-
- FDA. Food and Drug Administration Ozempic (semaglutide) injection prescribing information, revised. 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda _docs/label/2020/209637s003lbl... Published online 2020.
-
- Schaffer R., Heymsfield S.B.G.T.W. Healio website; 2021. FDA approves once-weekly semaglutide for weight loss. Published online.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources