Association between hypoglycemic agent use and the risk of occurrence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 37992029
- PMCID: PMC10664876
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294423
Association between hypoglycemic agent use and the risk of occurrence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
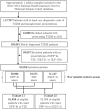
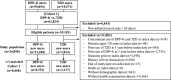
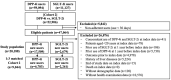
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern with increasing prevalence and associated health impacts. Although no approved drugs are available for the NAFLD treatment, several hypoglycemic agents have been investigated as promising therapeutic agents. We aimed to compare the risk of occurrence of NAFLD with respect to the use of different hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes. This retrospective cohort study used data from the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort of South Korea. Participants newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes (2003-2019) were included in this study. Two new user-active comparator cohorts were assembled: Cohort 1, new users of thiazolidinediones (TZD) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i), and Cohort 2, new users of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and DPP-4i. The occurrence of NAFLD was defined based claims that include diagnostic codes. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using Cox proportional hazard models in 1:3 propensity score (PS)-matched cohorts. For 65,224 patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, the overall prevalence of NAFLD was 42.6%. The PS-matched Cohort 1 included 6,351 and 2,117 new users of DPP-4i and TZD, respectively. Compared to DPP-4i, TZD use was associated with the decreased risk of NAFLD (HR, 0.66; 95% CI: 0.55-0.78). Cohort 2 consisted of 6,783 and 2,261 new users of DPP-4i and SGLT-2i, respectively; SGLT-2i use was associated with a decreased risk of NAFLD (HR, 0.93; 95% CI: 0.80-1.08). This population-based cohort study supports the clinical implications of prioritizing TZD and SGLT-2i over DPP-4i in reducing the risk of occurrence of NAFLD in patients with type 2 diabetes. However, the findings lacked statistical significance, highlighting the need for further verification studies.
Copyright: © 2023 Jung et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of SGLT-2i and GLP-1RA Therapy Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Varying NAFLD Status.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Dec 1;6(12):e2349856. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.49856. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 38153732 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and the risk of venous thromboembolism: A nationwide population-based study and meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024 Feb;40(2):e3739. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3739. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 37862117
-
A population-based cohort defined risk of hyperkalemia after initiating SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP1 receptor agonists or DPP-4 inhibitors to patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes.Kidney Int. 2024 Mar;105(3):618-628. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.11.025. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Kidney Int. 2024. PMID: 38101515 Free PMC article.
-
Should Baseline Hemoglobin A1c or Dose of SGLT-2i Guide Treatment With SGLT-2i Versus DPP-4i in People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;60(8):980-991. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1599. Epub 2020 May 12. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32396236
-
A Systematic Review of Newer Antidiabetic Agents in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Ann Pharmacother. 2021 Jan;55(1):65-79. doi: 10.1177/1060028020935105. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Ann Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 32571083
Cited by
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease risk with GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide nested case-control study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Oct 17;23(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02461-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39420429 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Risk-Prediction Model for Hypertension Patients Concomitant with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Apr 23;13(9):969. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13090969. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361747 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced hepatoprotective effects of empagliflozin and vitamin D dual therapy against metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis in mice by boosted modulation of metabolic, oxidative stress, and inflammatory pathways.Int J Exp Pathol. 2024 Dec;105(6):219-234. doi: 10.1111/iep.12519. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Int J Exp Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39397269
References
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al.. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328–57. Epub 2017/07/18. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- National interest disease statistics. [Internet]. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service (KR). Available from: http://opendata.hira.or.kr/op/opc/olapMfrnIntrsIlnsInfo.do.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical