Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2021
- PMID: 37992038
- PMCID: PMC10684357
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7209a1
Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2021
Abstract
Problem/condition: CDC conducts abortion surveillance to document the number and characteristics of women obtaining legal induced abortions and number of abortion-related deaths in the United States.
Period covered: 2021.
Description of system: Each year, CDC requests abortion data from the central health agencies for the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and New York City. For 2021, a total of 48 reporting areas voluntarily provided aggregate abortion data to CDC. Of these, 47 reporting areas provided data each year during 2012-2021. Census and natality data were used to calculate abortion rates (number of abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years) and ratios (number of abortions per 1,000 live births), respectively. Abortion-related deaths from 2020 were assessed as part of CDC's Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System (PMSS).
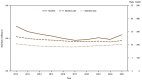
Results: A total of 625,978 abortions for 2021 were reported to CDC from 48 reporting areas. Among 47 reporting areas with data each year during 2012-2021, in 2021, a total of 622,108 abortions were reported, the abortion rate was 11.6 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years, and the abortion ratio was 204 abortions per 1,000 live births. From 2020 to 2021, the total number of abortions increased 5% (from 592,939 total abortions), the abortion rate increased 5% (from 11.1 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years), and the abortion ratio increased 4% (from 197 abortions per 1,000 live births). From 2012 to 2021, the total number of reported abortions decreased 8% (from 673,634), the abortion rate decreased 11% (from 13.1 abortions per 1,000 women aged 15-44 years), and the abortion ratio decreased 1% (from 207 abortions per 1,000 live births).In 2021, women in their 20s accounted for more than half of abortions (57.0%). Women aged 20-24 and 25-29 years accounted for the highest percentages of abortions (28.3% and 28.7%, respectively) and had the highest abortion rates (19.7 and 19.4 abortions per 1,000 women aged 20-24 and 25-29 years, respectively). By contrast, adolescents aged <15 years and women aged ≥40 years accounted for the lowest percentages of abortions (0.2% and 3.6%, respectively) and had the lowest abortion rates (0.4 and 2.5 abortions per 1,000 women aged <15 and ≥40 years, respectively). However, abortion ratios were highest among adolescents (aged ≤19 years) and lowest among women aged 30-39 years.From 2020 to 2021, abortion rates increased among women aged 20-39 years, decreased among adolescents aged 15-19 years, and did not change among adolescents aged <15 years and women aged ≥40 years. Abortion rates decreased from 2012 to 2021 among all age groups, except women aged 30-34 years for whom it increased. The decrease in the abortion rate from 2012 to 2021 was highest among adolescents compared with any other age group. From 2020 to 2021, abortion ratios increased for women aged 15-24 years, decreased among adolescents aged <15 years and women aged ≥35 years and did not change for women aged 25-34 years. From 2012 to 2021, abortion ratios increased among women aged 15-29 years and decreased among adolescents aged <15 years and women aged ≥30 years. The decrease in abortion ratio from 2012 to 2021 was highest among women aged ≥40 years compared with any other age group.In 2021, the majority (80.8%) of abortions were performed at ≤9 weeks' gestation, and nearly all (93.5%) were performed at ≤13 weeks' gestation. During 2012-2021, the percentage of abortions performed at >13 weeks' gestation remained ≤8.7%. In 2021, the highest percentage of abortions were performed by early medication abortion at ≤9 weeks' gestation (53.0%), followed by surgical abortion at ≤13 weeks' gestation (37.6%), surgical abortion at >13 weeks' gestation (6.4%), and medication abortion at >9 weeks' gestation (3.0%); all other methods were uncommon (<0.1%). Among those that were eligible (≤9 weeks' gestation), 66.6% of abortions were early medication abortions. In 2020, the most recent year for which PMSS data were reviewed for pregnancy-related deaths; six women died as a result of complications from legal induced abortion.
Interpretation: Among the 47 areas that reported data continuously during 2012-2021, overall decreases were observed during 2012-2021 in the total number, rate, and ratio of reported abortions; however, from 2020 to 2021, increases were observed across all measures.
Public health action: Abortion surveillance can be used to help evaluate programs aimed at promoting equitable access to patient-centered quality contraceptive services in the United States to reduce unintended pregnancies.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Gamble SB, Strauss LT, Parker WY, Cook DA, Zane SB, Hamdan S; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Abortion surveillance—United States, 2005. MMWR Surveill Summ 2008;57(No. SS-13):1–32. - PubMed
-
- Pazol K, Zane SB, Parker WY, Hall LR, Berg C, Cook DA; CDC. Abortion surveillance—United States, 2008. MMWR Surveill Summ 2011;60(No. SS-15):1–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
