Genetic newborn screening and digital technologies: A project protocol based on a dual approach to shorten the rare diseases diagnostic path in Europe
- PMID: 37992053
- PMCID: PMC10664952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293503
Genetic newborn screening and digital technologies: A project protocol based on a dual approach to shorten the rare diseases diagnostic path in Europe
Abstract
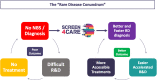
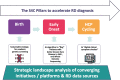
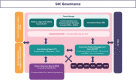
Since 72% of rare diseases are genetic in origin and mostly paediatrics, genetic newborn screening represents a diagnostic "window of opportunity". Therefore, many gNBS initiatives started in different European countries. Screen4Care is a research project, which resulted of a joint effort between the European Union Commission and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations. It focuses on genetic newborn screening and artificial intelligence-based tools which will be applied to a large European population of about 25.000 infants. The neonatal screening strategy will be based on targeted sequencing, while whole genome sequencing will be offered to all enrolled infants who may show early symptoms but have resulted negative at the targeted sequencing-based newborn screening. We will leverage artificial intelligence-based algorithms to identify patients using Electronic Health Records (EHR) and to build a repository "symptom checkers" for patients and healthcare providers. S4C will design an equitable, ethical, and sustainable framework for genetic newborn screening and new digital tools, corroborated by a large workout where legal, ethical, and social complexities will be addressed with the intent of making the framework highly and flexibly translatable into the diverse European health systems.
Copyright: © 2023 Garnier et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
none.
Figures

References
-
- The Power of being counted in: Rare-X Website. https://rare-x.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/be-counted-052722-WEB.pdf, Accessed 29 December 2022.
-
- EURORDIS Website. www.eurordis.org, Accessed 29 December 2022.

