Promoting physical activity and academic achievement through physically active learning: Qualitative perspectives of co-design and implementation processes
- PMID: 37992080
- PMCID: PMC10664963
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294422
Promoting physical activity and academic achievement through physically active learning: Qualitative perspectives of co-design and implementation processes
Abstract
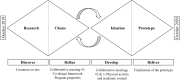
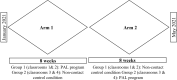
This article discussed the issue of low PA levels among school-aged children and highlights the promising approach of school-based interventions, including physically active learning (PAL), to increase PA levels. The study aimed to co-design and to assess the implementation of a PAL program for 8 weeks in 4 elementary classrooms (82 students and 7 teachers), emphasizing the potential of integrating PA with academic learning and the importance of co-designing programs with teachers to maximize their effectiveness. Technology was found to support PAL practices in promoting PA and academic achievement. The study underscores the need for further research to explore the societal implications of PAL programs, including their potential to improve the health and well-being of children while promoting positive academic outcomes.
Copyright: © 2023 Simard et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Cogni-Actif, the PAL program, has been co-designed in an action research project led by the authors. No other potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study protocol: the Fueling Learning through Exercise (FLEX) study - a randomized controlled trial of the impact of school-based physical activity programs on children's physical activity, cognitive function, and academic achievement.BMC Public Health. 2016 Oct 13;16(1):1078. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3719-0. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27737676 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Implementing physically active learning: Future directions for research, policy, and practice.J Sport Health Sci. 2020 Jan;9(1):41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2019.05.007. Epub 2019 May 24. J Sport Health Sci. 2020. PMID: 31921479 Free PMC article.
-
Behaviours that prompt primary school teachers to adopt and implement physically active learning: a meta synthesis of qualitative evidence.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021 Nov 20;18(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12966-021-01221-9. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021. PMID: 34801039 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Activity in High School Classrooms: A Promising Avenue for Future Research.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 8;19(2):688. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020688. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35055510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effects of physically active classrooms on educational and enjoyment outcomes in school age children.PLoS One. 2019 Jun 25;14(6):e0218633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218633. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31237913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increasing adolescents' physical activity levels through a comprehensive school-based physical activity program: study protocol of the cluster randomized controlled trial Active School.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05034-0. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39232723 Free PMC article.
-
A study on the relationship between physical exercise and feelings of inferiority among college students: the chain mediating effect of social support and emotional regulation ability.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1521510. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1521510. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39850972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaput J-P, Willumsen J, Bull F, Chou R, Ekelund U, Firth J, et al.. 2020 WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour for children and adolescents aged 5–17 years: summary of the evidence. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity. 2020;17(1):1–9. 10.1186/s12966-020-01037-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colley RC, Carson V, Garriguet D, Janssen I, Roberts KC, Tremblay MS. Physical activity of Canadian children and youth, 2007 to 2015: Statistics Canada Ottawa, ON, Canada; 2017. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources