Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia/multifocal leukoplakia in patients with and without oral submucous fibrosis
- PMID: 37992140
- PMCID: PMC10765335
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.26106
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia/multifocal leukoplakia in patients with and without oral submucous fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF) and proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL) are established as oral potentially malignant disorders. Dual pathology of the two conditions is not commonly encountered in clinical practice. This study aims to present a case series of multifocal leukoplakia in patients with and without OSF to outline the clinical behavior and challenges in the management of this high-risk group in clinical practice.
Material and methods: We retrospectively analyzed cases of six Indian patients (four with OSF) managed over a period of 5.5 to 13 years at the Government Dental College, Nagpur. Patient data consisting of age, gender, medical history, habits, clinical findings, and biopsy reports were recorded at the initial visit. During follow-up visits, the clinicopathological data were reassessed. When surgical intervention failed to arrest the disease or when surgery was contraindicated metronomic therapy with Folitrax 15 mg once a week and Celecoxib 100mg twice daily was initiated.
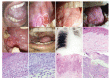
Results: All patients developed PVL after the initial pathology diagnosis of OSF or oral leukoplakia. Initial lesions were either homogenous or non-homogenous leukoplakia. All patients developed multiple recurrences, regional or systemic metastasis. Despite thorough interventions, the patients died of, or with the disease.
Conclusions: The occurrence of two or more oral potentially malignant disorders poses challenges in patient management and possibly presents a higher risk of malignant transformation. More clinical trials are necessary to assess the benefits of metronomic therapy for patients diagnosed with aggressive PVL concurrently found with OSF.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest All authors declare they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mello FW, Miguel AFP, Dutra KL, Porporatti AL, Warnakulasuriya S, Guerra ENS. Prevalence of oral potentially malignant disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018;47:633. - PubMed
-
- Yang YH, Lee HY, Tung S, Shieh TY. Epidemiological survey of oral submucous fibrosis and leukoplakia in aborigines of Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med. 2001;30:213–9. - PubMed
-
- Hazarey VK, Erlewad DM, Mundhe K, Ughade SN. Oral submucous fibrosis: A study of 1000 cases from central India. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

