Elastomeric vitrimers from designer polyhydroxyalkanoates with recyclability and biodegradability
- PMID: 37992173
- PMCID: PMC10664982
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adi1735
Elastomeric vitrimers from designer polyhydroxyalkanoates with recyclability and biodegradability
Abstract
Cross-linked elastomers are stretchable materials that typically are not recyclable or biodegradable. Medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates (mcl-PHAs) are soft and ductile, making these bio-based polymers good candidates for biodegradable elastomers. Elasticity is commonly imparted by a cross-linked network structure, and covalent adaptable networks have emerged as a solution to prepare recyclable thermosets via triggered rearrangement of dynamic covalent bonds. Here, we develop biodegradable and recyclable elastomers by chemically installing the covalent adaptable network within biologically produced mcl-PHAs. Specifically, an engineered strain of Pseudomonas putida was used to produce mcl-PHAs containing pendent terminal alkenes as chemical handles for postfunctionalization. Thiol-ene chemistry was used to incorporate boronic ester (BE) cross-links, resulting in PHA-based vitrimers. mcl-PHAs cross-linked with BE at low density (<6 mole %) affords a soft, elastomeric material that demonstrates thermal reprocessability, biodegradability, and denetworking at end of life. The mechanical properties show potential for applications including adhesives and soft, biodegradable robotics and electronics.
Figures
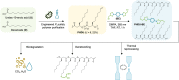
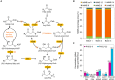


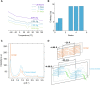
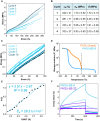

References
-
- S. Y. Choi, I. J. Cho, Y. Lee, Y.-J. Kim, K.-J. Kim, S. Y. Lee, Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates and nonnatural polyesters. Adv. Mater. 32, e1907138 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Y. Zheng, J. C. Chen, Y. M. Ma, G. Q. Chen, Engineering biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) for diversity and cost reduction. Metab. Eng. 58, 82–93 (2020). - PubMed
-
- A. Prieto, I. F. Escapa, V. Martinez, N. Dinjasky, C. Herencias, F. de la Peña, N. Tarazona, O. Revelles, A holistic view of polyhydroxyalkanoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida. Environ. Microbiol. 18, 341–357 (2016). - PubMed
-
- R. M. Cywar, N. A. Rorrer, C. B. Hoyt, G. T. Beckham, E. Y.-X. Chen, Bio-based polymers with performance-advantaged properties. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 83–103 (2022).
-
- M. Li, Y. Ma, X. Zhang, L. Zhang, X. Chen, J.-W. Ye, G.-Q. Chen, Tailor-made polyhydroxyalkanoates by reconstructing Pseudomonas entomophila. Adv. Mater. 33, e2102766 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

