Burden of AML, 1990-2019: Estimates From the Global Burden of Disease Study
- PMID: 37992271
- PMCID: PMC10681472
- DOI: 10.1200/GO.23.00229
Burden of AML, 1990-2019: Estimates From the Global Burden of Disease Study
Abstract
Purpose: AML accounts for 80% of acute leukemia in adults. While progress has been made in treating younger patients in the past 2 decades, there has been limited improvement for older patients until recently. This study examines the global and European Union (EU) 15+ trends in AML between 1990 and 2019.
Methods: We extracted age-standardized incidence rates (ASIRs), age-standardized death rates (ASMRs), and disability-adjusted life years, stratified by sex from the Global Burden of Disease Study database, and mortality-to-incidence ratio (MIR) were computed. Trends were compared using Joinpoint regression.
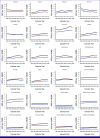
Results: The findings show a global increase in AML incidence for both sexes from 1990 to 2019. In the EU15+ countries, most countries exhibited an increase in ASIR for both sexes. Joinpoint revealed that globally for male patients, ASIR steadily increased until 2010, remained stable until 2015 followed by a decline till 2019. Similar trends were observed in female patients. For ASMR, although there was an increase globally and in most EU15+ countries, there was a statistically significant decrease in mortality rates globally and in the majority of EU15+ countries in recent years. MIR improved in both sexes globally. On age stratification, AML burden was highest among older groups (55 years and older), while the lowest rates were observed in younger than 20 years.
Conclusion: The findings from our study indicate a global rise in AML incidence and mortality in both sexes and decrease in MIR from 1990 to 2019 suggesting a better survival. However, on Joinpoint analysis, there is no change in MIR in women in the past decade and past 4 years in men indicating plateau in survival trends despite recent advances.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html
-
- Ferlay J Soerjomataram I Dikshit R, et al. : Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359-E386, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7-30, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

