Cancer organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction (CODRP) index-based anticancer drug sensitivity test in ALK-rearrangement positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 37993887
- PMCID: PMC10664561
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02899-4
Cancer organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction (CODRP) index-based anticancer drug sensitivity test in ALK-rearrangement positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Erratum in
-
Correction: Cancer organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction (CODRP) index-based anticancer drug sensitivity test in ALK-rearrangement positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 6;42(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02919-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38057916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Recently, cancer organoid-based drug sensitivity tests have been studied to predict patient responses to anticancer drugs. The area under curve (AUC) or IC50 value of the dose-response curve (DRC) is used to differentiate between sensitive and resistant patient's groups. This study proposes a multi-parameter analysis method (cancer organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction, CODRP) that considers the cancer stage and cancer cell growth rate, which represent the severity of cancer patients, in the sensitivity test.
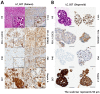
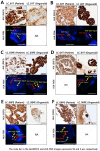
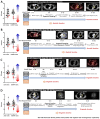
Methods: On the CODRP platform, patient-derived organoids (PDOs) that recapitulate patients with lung cancer were implemented by applying a mechanical dissociation method capable of high yields and proliferation rates. A disposable nozzle-type cell spotter with efficient high-throughput screening (HTS) has also been developed to dispense a very small number of cells due to limited patient cells. A drug sensitivity test was performed using PDO from the patient tissue and the primary cancer characteristics of PDOs were confirmed by pathological comparision with tissue slides.
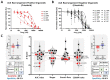
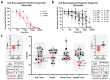
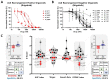
Results: The conventional index of drug sensitivity is the AUC of the DRC. In this study, the CODRP index for drug sensitivity test was proposed through multi-parameter analyses considering cancer cell proliferation rate, the cancer diagnosis stage, and AUC values. We tested PDOs from eight patients with lung cancer to verify the CODRP index. According to the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangement status, the conventional AUC index for the three ALK-targeted drugs (crizotinib, alectinib, and brigatinib) did not classify into sensitive and resistant groups. The proposed CODRP index-based drug sensitivity test classified ALK-targeted drug responses according to ALK rearrangement status and was verified to be consistent with the clinical drug treatment response.
Conclusions: Therefore, the PDO-based HTS and CODRP index drug sensitivity tests described in this paper may be useful for predicting and analyzing promising anticancer drug efficacy for patients with lung cancer and can be applied to a precision medicine platform.
Keywords: 3D cell culture; Cancer Organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction (CODRP) platform; High-throughput screening (HTS); Non-small cell Lung cancer (NSCLC); Patient-derived Organoid (PDO).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prediction of TKI response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer patients-derived organoids using malignant pleural effusion.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 May 21;8(1):111. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00609-7. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38773241 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and safety of brigatinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer and other malignancies: a single-arm, open-label, phase 1/2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Dec;17(12):1683-1696. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30392-8. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27836716 Clinical Trial.
-
Resistance profiles of anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicenter study using targeted next-generation sequencing.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Oct;156:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.043. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34392186
-
Canadian perspectives: update on inhibition of ALK-positive tumours in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Curr Oncol. 2018 Oct;25(5):317-328. doi: 10.3747/co.25.4379. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Curr Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30464681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer: a focus on ALK/ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018 Jan;18(1):71-80. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2018.1412260. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29187012 Review.
Cited by
-
From Cancer to Immune Organoids: Innovative Preclinical Models to Dissect the Crosstalk between Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10823. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910823. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung cancer organoid-based drug evaluation models and new drug development application trends.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):3741-3763. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-603. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39830742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryopreservation of human lung tissue for 3D ex vivo analysis.Respir Res. 2025 May 15;26(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03265-y. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40375251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung cancer organoids: a new strategy for precision medicine research.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):575-590. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-921. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40114941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction: Cancer organoid-based diagnosis reactivity prediction (CODRP) index-based anticancer drug sensitivity test in ALK-rearrangement positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 6;42(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02919-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38057916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhang X, Zhang S, Yang X, Yang J, Zhou Q, Yin L, An S, Lin J, Chen S, Xie Z, et al. Fusion of EML4 and ALK is associated with development of lung adenocarcinomas lacking EGFR and KRAS mutations and is correlated with ALK expression. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:188. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Inamura K, Takeuchi K, Togashi Y, Hatano S, Ninomiya H, Motoi N, Mun MY, Sakao Y, Okumura S, Nakagawa K, et al. EML4-ALK Lung Cancers are characterized by rare other mutations, a TTF-1 cell lineage, an acinar histology, and young onset. Mod Pathol. 2009;22:508–15. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Li Y, Yang T, Wei S, Wang J, Wang M, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Liu H, Chen J. Clinical significance of EML4-ALK fusion gene and association with EGFR and KRAS gene mutations in 208 Chinese patients with non-small cell Lung cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e52093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052093. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019M3A9H2032425/the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT)
- 2020R1I1A306655012/the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT)
- (2022) ERIC07_1_1/the Ministry of Science and ICT and Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

