Exploring amygdala structural changes and signaling pathways in postmortem brains: consequences of long-term methamphetamine addiction
- PMID: 37994041
- PMCID: PMC10968194
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.23.193
Exploring amygdala structural changes and signaling pathways in postmortem brains: consequences of long-term methamphetamine addiction
Abstract
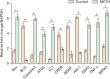
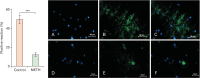
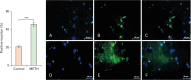
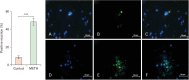
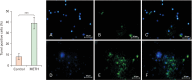
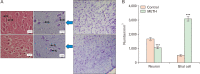
Methamphetamine (METH) can potentially disrupt neurotransmitters activities in the central nervous system (CNS) and cause neurotoxicity through various pathways. These pathways include increased production of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species, hypothermia, and induction of mitochondrial apoptosis. In this study, we investigated the long-term effects of METH addiction on the structural changes in the amygdala of postmortem human brains and the involvement of the brain- cAMP response element-binding protein/brain-derived neurotrophic factor (CREB/BDNF) and Akt-1/GSK3 signaling pathways. We examined ten male postmortem brains, comparing control subjects with chronic METH users, using immunohistochemistry, real-time polymerase chain reaction (to measure levels of CREB, BDNF, Akt-1, GSK3, and tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]), Tunnel assay, stereology, and assays for reactive oxygen species (ROS), glutathione disulfide (GSSG), and glutathione peroxidase (GPX). The findings revealed that METH significantly reduced the expression of BDNF, CREB, Akt-1, and GPX while increasing the levels of GSSG, ROS, RIPK3, GSK3, and TNF-α. Furthermore, METH-induced inflammation and neurodegeneration in the amygdala, with ROS production mediated by the CREB/BDNF and Akt-1/GSK3 signaling pathways.
Keywords: Amygdala; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Methamphetamine; cAMP response element-binding protein.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pharmacological evidence for lithium-induced neuroprotection against methamphetamine-induced neurodegeneration via Akt-1/GSK3 and CREB-BDNF signaling pathways.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Aug;22(8):856-865. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2019.30855.7442. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31579440 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of metformin against methamphetamine induced anxiety, depression, cognition impairment and neurodegeneration in rat: The role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways.Neurotoxicology. 2019 May;72:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30742852
-
Neuroprotective Properties of Minocycline Against Methylphenidate-Induced Neurodegeneration: Possible Role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 Signaling Pathways in Rat Hippocampus.Neurotox Res. 2022 Jun;40(3):689-713. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00454-7. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35446003
-
Novel Insight to Neuroprotective Potential of Curcumin: A Mechanistic Review of Possible Involvement of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and PI3/Akt/ GSK3 or PI3/Akt/CREB/BDNF Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2020 Winter;9(1):1-32. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.9.1.1. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2020. PMID: 32832482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Levo-tetrahydropalmatine: A new potential medication for methamphetamine addiction and neurotoxicity.Exp Neurol. 2021 Oct;344:113809. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113809. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34256045 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant-derived polyphenolic compounds for managing schizophrenia: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 19;16:1605027. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605027. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40612741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Behl T, Makkar R, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Zengin G, Bungau S, Andronie-Cioara FL, Munteanu MA, Brisc MC, Uivarosan D, Brisc C. Current trends in neurodegeneration: cross talks between oxidative stress, cell death, and inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:7432. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pourgholaminejad A, Tahmasebinia F. The role of Th17 cells in immunopathogenesis of neuroinflammatory disorders. In: Mitoma H, Manto M, editors. Neuroimmune Diseases: From Cells to the Living Brain. Springer; 2019. pp. 83–107. - DOI
-
- Mahmoudiasl GR, Abbaszadeh HA, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Abdollahifar MA, Khoramgah MS, Niknazar S, Darabi S, Roozbahany NA. Nod-like receptor protein 3 and nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome activation in the hippocampal region of postmortem methamphetamine chronic user. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2019;120:769–76. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2019_129. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khoshsirat S, Khoramgah MS, Mahmoudiasl GR, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Abdollahifar MA, Tahmasebinia F, Darabi S, Niknazar S, Abbaszadeh HA. LC3 and ATG5 overexpression and neuronal cell death in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem chronic methamphetamine users. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;107:101802. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101802. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
