A novel nomogram and risk stratification for early metastasis in cervical cancer after radical radiotherapy
- PMID: 37994611
- PMCID: PMC10757092
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.6745
A novel nomogram and risk stratification for early metastasis in cervical cancer after radical radiotherapy
Abstract
Object: This study aimed to establish an effective risk nomogram to predict the early distant metastasis (EDM) probability of cervical cancer (CC) patients treated with radical radiotherapy to aid individualized clinical decision-making.
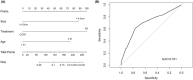
Methods: A total of 489 patients with biopsy-confirmed CC between December 2018 and January 2021 were enrolled. Logistic regression with the stepwise backward method was used to identify independent risk factors. The nomogram efficacy was evaluated by using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), C-index by 1000 bootstrap replications, etc. Finally, patients were divided into high- and low-risk groups of EDM based on the cut-off value of nomogram points.
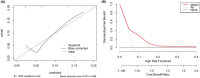
Results: 36 (7.36%) CC patients had EDM, and 20 (55.6%) EDM had more than one metastatic site involved. Age below 51 (OR = 2.298, p < 0.001), tumor size larger than 4.5 cm (OR = 3.817, p < 0.001) and radiotherapy (OR = 3.319, p < 0.001) were independent risk factors of EDM. For the nomogram model, C-index was 0.701 (95% CI = 0.604-0.798), and 0.675 (95% CI = 0.578-0.760) after 1000 bootstrap resampling validations. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test demonstrated no overfitting (p = 0.924). According to the Kaplan-Meier curve of risk score, patients with high risk were more prone to get EDM (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: This is the first research to focus on EDM in CC patients. We have developed a robust scoring system to predict the risk of EDM in CC patients to screen out appropriate cases for consolidation therapy and more intensive follow-up.
Keywords: cervical cancer; early distant metastasis; prognostic model; radiotherapy; risk factors.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Establishment and validation of a novel nomogram to predict overall survival after radical nephrectomy].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023 Aug 23;45(8):681-689. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20221027-00722. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37580273 Chinese.
-
[Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram model for advanced gastric cancer with perineural invasion].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Nov 25;23(11):1059-1066. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200103-00004. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33212554 Chinese.
-
A novel nomogram based on inflammation biomarkers for predicting radiation cystitis in patients with local advanced cervical cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 May;13(10):e7245. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7245. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38785171 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of risk evaluation model of peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer and its predictive value].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jan 25;20(1):47-52. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28105619 Chinese.
-
Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Predicting Postoperative Distant Metastasis in Patients with Cervical Cancer.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Apr 12;28:e933379. doi: 10.12659/MSM.933379. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35410987 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Causes of death analysis and the prognostic model construction in neuroendocrine carcinoma of the cervix: A SEER-based study.Cancer Med. 2024 Aug;13(15):e70066. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70066. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39118477 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal MRI-based deep-radiomics model predicts response in cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 17;14(1):19090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70055-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39154103 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Invasion Distance Based on MRI Is a Novel Prognostic Indicator for I-IIIB Cervical Cancer Patients Treated with Radiotherapy.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;32(6):355. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32060355. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40558298 Free PMC article.
-
A Diagnostic Nomogram Incorporating Prognostic Nutritional Index for Predicting Vaginal Invasion in Stage IB - IIA Cervical Cancer.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241278479. doi: 10.1177/10732748241278479. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39171582 Free PMC article.
-
A surprising complete response to cadonilimab in a primary metastatic cervical cancer: a case report.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 26;15:1494138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1494138. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39660134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Okazawa‐Sakai M, Mabuchi S, Isohashi F, et al. Predictors of distant relapse in patients with FIGO stage IIB‐IVA cervical cancer treated with definitive radiotherapy. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2017;43(11):1743‐1750. - PubMed

