A Digital Single-Session Intervention (Project Engage) to Address Fear of Negative Evaluation Among College Students: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37995114
- PMCID: PMC10704327
- DOI: 10.2196/48926
A Digital Single-Session Intervention (Project Engage) to Address Fear of Negative Evaluation Among College Students: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Increasingly, college science courses are transitioning from a traditional lecture format to active learning because students learn more and fail less frequently when they engage in their learning through activities and discussions in class. Fear of negative evaluation (FNE), defined as a student's sense of dread associated with being unfavorably evaluated while participating in a social situation, discourages undergraduates from participating in small group discussions, whole class discussions, and conversing one-on-one with instructors.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the acceptability of a novel digital single-session intervention and to assess the feasibility of implementing it in a large enrollment college science course taught in an active learning way.
Methods: To equip undergraduates with skills to cope with FNE and bolster their confidence, clinical psychologists and biology education researchers developed Project Engage, a digital, self-guided single-session intervention for college students. It teaches students strategies for coping with FNE to bolster their confidence. Project Engage provides biologically informed psychoeducation, uses interactive elements for engagement, and helps generate a personalized action plan. We conducted a 2-armed randomized controlled trial to evaluate the acceptability and the preliminary effectiveness of Project Engage compared with an active control condition that provides information on available resources on the college campus.
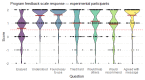
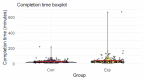
Results: In a study of 282 upper-level physiology students, participants randomized to complete Project Engage reported a greater increase in overall confidence in engaging in small group discussions (P=.01) and whole class discussions (P<.001), but not in one-on-one interactions with instructors (P=.05), from baseline to immediately after intervention outcomes, compared with participants in an active control condition. Project Engage received a good acceptability rating (1.22 on a scale of -2 to +2) and had a high completion rate (>97%).
Conclusions: This study provides a foundation for a freely available, easily accessible intervention to bolster student confidence for contributing in class.
Trial registration: OSF Registries osf.io/4ca68 http://osf.io/4ca68.
Keywords: active learning; active learning course; college student; fear of negative evaluation; intervention; negative evaluation; pilot randomized controlled trial; science course; single-session intervention.
©Arka Ghosh, Katherine A Cohen, Laura Jans, Carly A Busch, Riley McDanal, Yuanyuan Yang, Katelyn M Cooper, Jessica L Schleider. Originally published in JMIR Mental Health (https://mental.jmir.org), 23.11.2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: JLS serves on the Scientific Advisory Board for Walden Wise and the Clinical Advisory Board for Koko; receives consulting fees from Kooth, LLC and Woebot Health; is the cofounder and codirector of Single Session Support Solutions; and receives book royalties from New Harbinger, Oxford University Press, and Little Brown Book Group. KAC receives consulting fees from Kooth, LLC and Koko.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Disproportionate Impact of Fear of Negative Evaluation on First-Generation College Students, LGBTQ+ Students, and Students with Disabilities in College Science Courses.CBE Life Sci Educ. 2023 Sep;22(3):ar31. doi: 10.1187/cbe.22-10-0195. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2023. PMID: 37347813 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of active learning practices on student anxiety in large-enrollment college science classrooms.Int J STEM Educ. 2018;5(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s40594-018-0123-6. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Int J STEM Educ. 2018. PMID: 30631713 Free PMC article.
-
Call on me! Undergraduates' perceptions of voluntarily asking and answering questions in front of large-enrollment science classes.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 12;16(1):e0243731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243731. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33434226 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current and Future Approaches to Pediatric Anxiety Disorder Treatment.Am J Psychiatry. 2024 Mar 1;181(3):189-200. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.20231037. Am J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38425255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance of Digital Mental Health Interventions for College Students: A Systematic Review.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024 Dec;26(12):683-693. doi: 10.1007/s11920-024-01545-w. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2024. PMID: 39392547 Free PMC article.
-
Student identities predict classmate and instructor fear of negative evaluation among undergraduates in large-enrollment introductory biology courses.J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2025 Aug 21;26(2):e0019124. doi: 10.1128/jmbe.00191-24. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2025. PMID: 40293234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: a call to action. The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) 2009. [2023-11-04]. https://www.aaas.org/sites/default/files/content_files/VC_report.pdf .
-
- Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: chronicling change, inspiring the future. The American Association for the Advancement of Science. 2015. [2023-11-04]. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=3f3a12e5... .
-
- Driessen EP, Knight JK, Smith MK, Ballen CJ. Demystifying the meaning of active learning in postsecondary biology education. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2020 Dec;19(4):ar52. doi: 10.1187/cbe.20-04-0068. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33001767 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Freeman S, Eddy SL, McDonough M, Smith MK, Okoroafor N, Jordt H, Wenderoth MP. Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jun 10;111(23):8410–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319030111. https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.1319030111?url_ver=Z39.88-2003... 1319030111 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Theobald EJ, Hill MJ, Tran E, Agrawal S, Arroyo EN, Behling S, Chambwe N, Cintrón DL, Cooper JD, Dunster G, Grummer JA, Hennessey K, Hsiao J, Iranon N, Jones L, Jordt H, Keller M, Lacey ME, Littlefield CE, Lowe A, Newman S, Okolo V, Olroyd S, Peecook BR, Pickett SB, Slager DL, Caviedes-Solis IW, Stanchak KE, Sundaravardan V, Valdebenito C, Williams CR, Zinsli K, Freeman S. Active learning narrows achievement gaps for underrepresented students in undergraduate science, technology, engineering, and math. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 24;117(12):6476–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1916903117. https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.1916903117?url_ver=Z39.88-2003... 1916903117 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

